Portefaix Documentation Welcome to the Portefaix documentation! Here you’ll find everything you need to know about Portefaix, from getting started to advanced topics.
Visit the tutorials for guided learning paths to try out Portefaix and pick up the main concepts.
Check out the how-to guides for step-by-step instructions on how to use Portefaix and its features.
Refer to detailed information on Portefaix resources, repositories, FAQs, and more.
1 - Tutorials Follow along with a set of tutorials to learn how to use the Portefaix project
2 - How-To guides Learn how to use Portefaix with detailed guides
2.1 - Portefaix Infrastructure Learn about deploying Portefaix infrastructure
2.1.1 - Amazon Web Services Running Portefaix on Amazon Web Services
2.1.1.1 - Overview Portefaix architecture on Amazon Web Services
2.1.1.2 - Install on Amazon Web Services Running Portefaix on Amazon Web Services
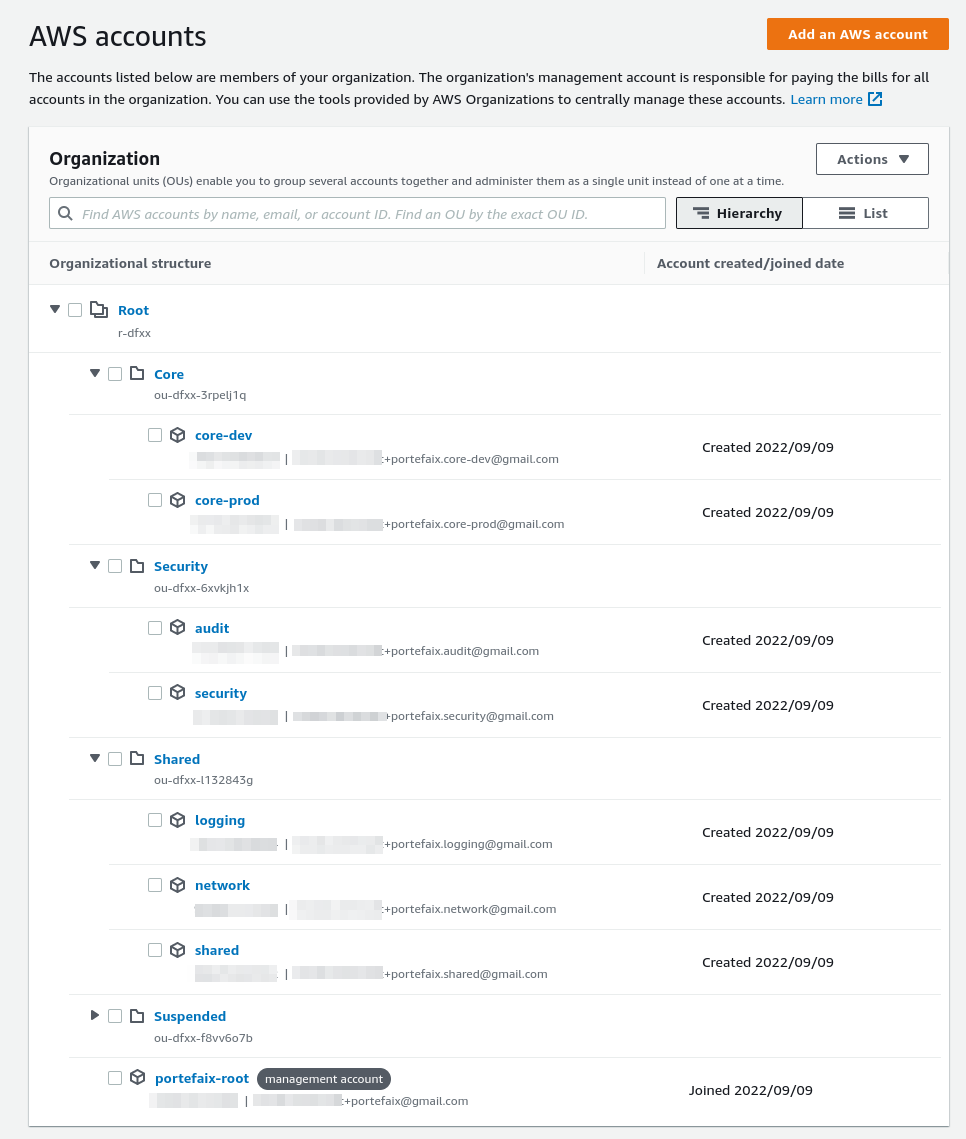
Setup Creates an AWS Organization , and enable Service Control Policies in AWS organizations.
Now that we’ve created an organization, you’ll notice that all the policies are disabled by default.
There you need to enable AWS Service Control Policies in the AWS console by clicking on the button Enable service control policies. Do the same action for the AWS Tag Policies.
Navigate to Personal Health Dashboard service in the console. On the left side panel, expand Organizational view and choose configurations. Then, enable organizational view for AWS Health
Create an admin user , and configure account alias for IAM Users access
Then API Keys .
Configure Portefaix environment file ${HOME}/.config/portefaix/portefaix.sh:
HOME_IP = $( curl -s http://ifconfig.me)
SLACK_WEBHOOK_NOTIFS = "https://hooks.slack.com/services/xxx/xxx"
# AWS
function setup_aws() {
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = "....."
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = "....."
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION = "..."
export AWS_REGION = "...."
# For Terraform Cloud
export TF_VAR_access_key = " ${ AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID } "
export TF_VAR_secret_key = " ${ AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY } "
export TF_VAR_slack_webhook_url = " ${ SLACK_WEBHOOK_NOTIFS } "
export TF_VAR_org_email = "xxxxxx" # for Root Account
export TF_VAR_org_email_domain = "gmail.com"
export TF_VAR_org_admin_username = "xxxxxx"
export TF_VAR_admin_ipv4 = "[\" ${ HOME_IP } /32\"]" # for WAF
}
Load environment :
Create a S3 bucket for Terraform states:
❯ make -f hack/build/aws.mk aws-s3-bucket ENV = staging
Create a DynamoDB table :
❯ make -f hack/build/aws.mk aws-dynamodb-create-table ENV = staging
AWS Organization Units and Accounts Configure the AWS Organization:
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/aws/root ENV = main
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/aws/terraform-cloud ENV = main
Authentication Kubernetes Configure the AWS provider
❯ . ./portefaix.sh aws
[ Portefaix ]
Setup credentials
Done
Perform an AWS authentication:
❯ make -f hack/build/aws.mk ENV = staging aws-admin
source ./hack/scripts/aws-auth.sh xxxxxx Administrator portefaix-staging-eks eu-west-1
❯ source ./hack/scripts/aws-auth.sh xxxxxxx Administrator portefaix-staging-eks eu-west-1
Update Kubernetes configuration file:
❯ make -f hack/build/aws.mk ENV = staging aws-kube-credentials
❯ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-10-0-13-85.eu-west-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 81m v1.23.9-eks-ba74326
ip-10-0-29-115.eu-west-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 81m v1.23.9-eks-ba74326
ip-10-0-60-137.eu-west-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 81m v1.23.9-eks-ba74326
ip-10-0-70-76.eu-west-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 81m v1.23.9-eks-ba74326
Bastion You would use the AWS System Manager plugin to connect to EC2 and EKS instances:
❯ aws ec2 describe-instances --output table
-------------------
| DescribeInstances|
+-----------------+
❯ aws ssm start-session --target i-019042b3847f5c81f
Starting session with SessionId: portefaix-admin-031b2ba6d981142b0
Gitops for Kubernetes Next: Gitops
Inspec Inspec is used to check infrastructure.
Check:
❯ make -f hack/build/aws.mk inspec-debug
Test infrastructure
────────────────────────────── Platform Details ──────────────────────────────
Name: aws
Families: cloud, api
Release: train-aws: v0.1.15, aws-sdk-core: v3.94.0
Execute tests:
❯ make -f hack/build/aws.mk inspec-test SERVICE = iac/aws/<SERVICE> ENV = staging
You could upload JSON results file to Heimdall Lite to display ressults
CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark You could perform tests according to the CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark :
❯ make -f hack/build/aws.mk inspec-aws-cis ENV = staging
CIS Kubernetes Benchmark
❯ make -f hack/build/aws.mk inspec-aws-kubernetes ENV = staging
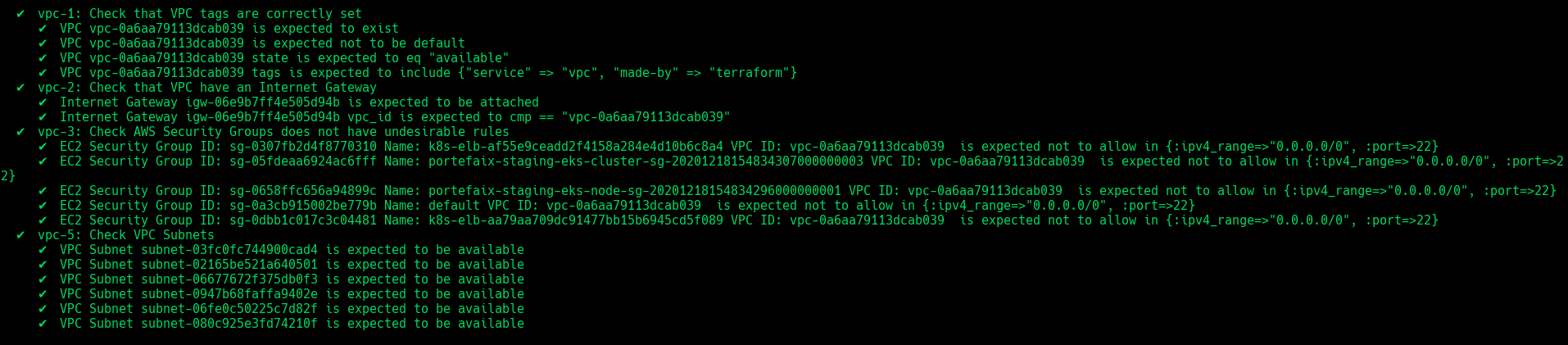
VPC
❯ make -f hack/build/aws.mk inspec-test SERVICE = iac/aws/vpc ENV = staging
Code Description vpc-1Ensure that VPC exist and tags correcly set vpc-2Ensure that VPC have an Internet Gateway vpc-3Check AWS Security Groups does not have undesirable rules vpc-4Ensure that VPC Subnets exists
EKS
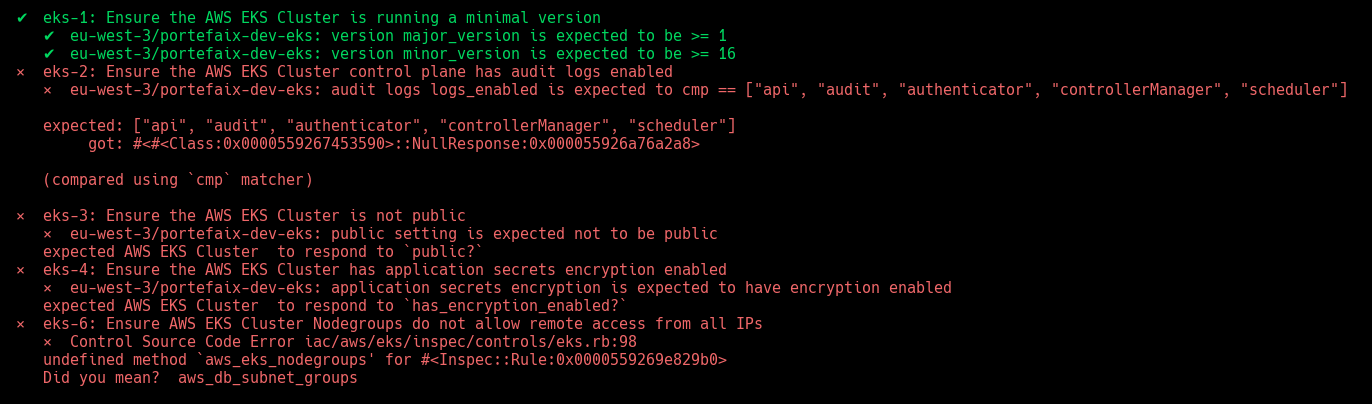
❯ make -f hack/build/aws.mk inspec-test SERVICE = iac/aws/eks ENV = staging
Code Description eks-1Ensure the AWS EKS Cluster is running a minimal version eks-2Ensure the AWS EKS Cluster control plane has audit logs enabled eks-3Ensure the AWS EKS Cluster is not public eks-4Ensure the AWS EKS Cluster has application secrets encryption enabled eks-5Ensure AWS EKS Cluster Subnets are specific eks-6Ensure AWS EKS Cluster Nodegroups do not allow remote access from all IPs
Observability
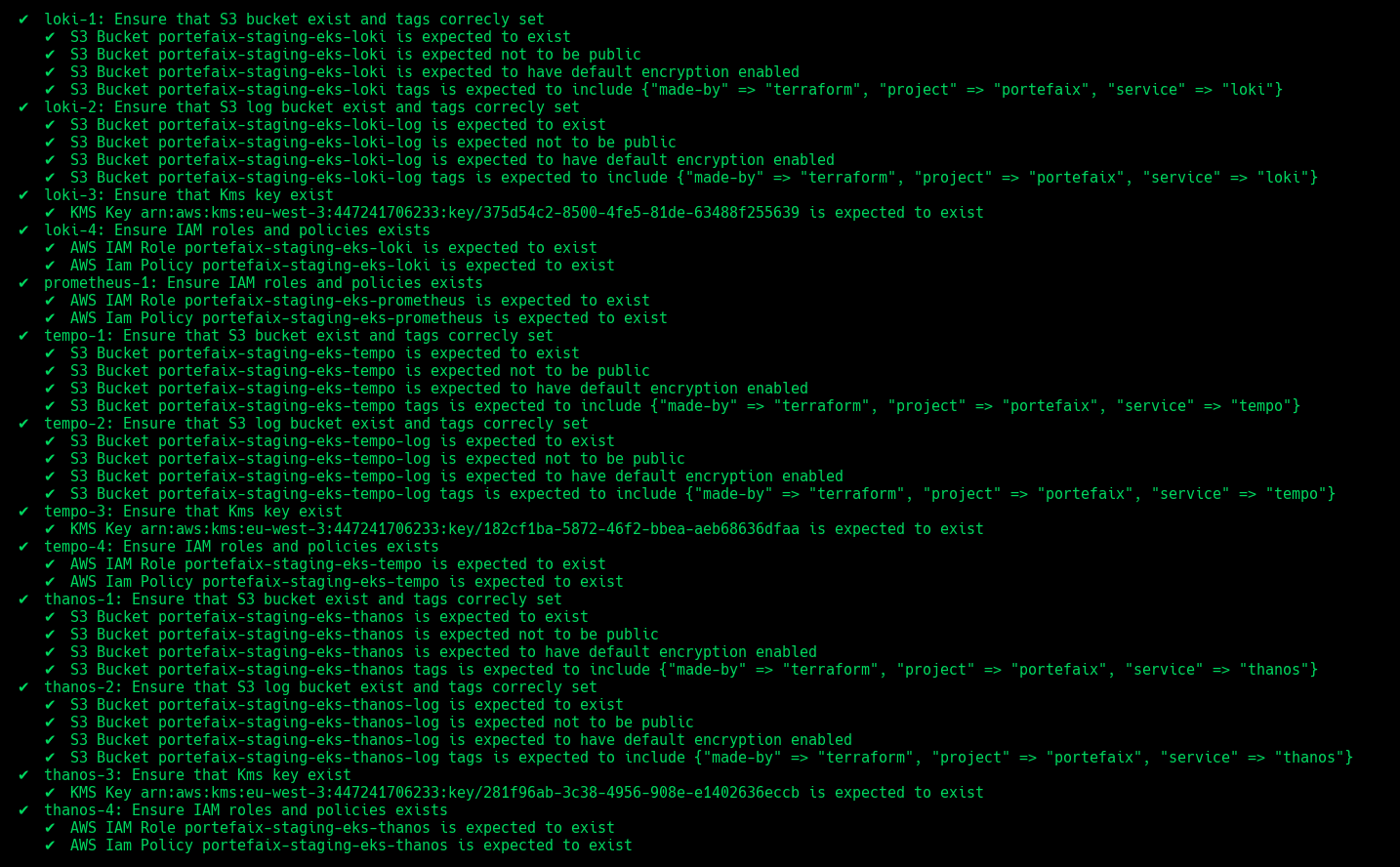
❯ make -f hack/build/aws.mk inspec-test SERVICE = iac/aws/observability ENV = staging
Code Description grafana-1Ensure IAM roles and policies exists prometheus-1Ensure IAM roles and policies exists thanos-1Ensure that S3 bucket exist and tags correcly set thanos-2Ensure that S3 log bucket exist and tags correcly set thanos-3Ensure that Kms key exist thanos-4Ensure IAM roles and policies exists loki-1Ensure that S3 bucket exist and tags correcly set loki-2Ensure that S3 log bucket exist and tags correcly set loki-3Ensure that Kms key exist loki-4Ensure IAM roles and policies exists tempo-1Ensure that S3 bucket exist and tags correcly set tempo-2Ensure that S3 log bucket exist and tags correcly set tempo-3Ensure that Kms key exist tempo-4Ensure IAM roles and policies exists
2.1.2 - Microsoft Azure Running Portefaix on Azure
2.1.2.1 - Overview Portefaix architecture on Microsoft Azure
2.1.2.2 - Install on Microsoft Azure Running Portefaix on Microsoft Azure
Setup Export Azure credentials:
❯ export AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID = "xxxxxx"
create a service principal:
❯ make -f hack/build/azure.mk azure-sp
The appId, password, and tenant values are used in the next step:
export ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID = "<azure_subscription_id>"
export ARM_TENANT_ID = "<azure_subscription_tenant_id>"
export ARM_CLIENT_ID = "<service_principal_appid>"
export ARM_CLIENT_SECRET = "<service_principal_password>"
Create a Storage Account :
❯ make -f hack/build/azure.mk azure-storage-account
XXXXXXXXXXX
You could see the Key on the output.
Create storage container for Terraform states:
❯ make -f hack/build/azure.mk azure-storage-container AZ_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_KEY = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
Set permissions:
❯ make -f hack/build/azure.mk azure-permissions
Enable preview features:
❯ make -f hack/build/azure.mk azure-wasi
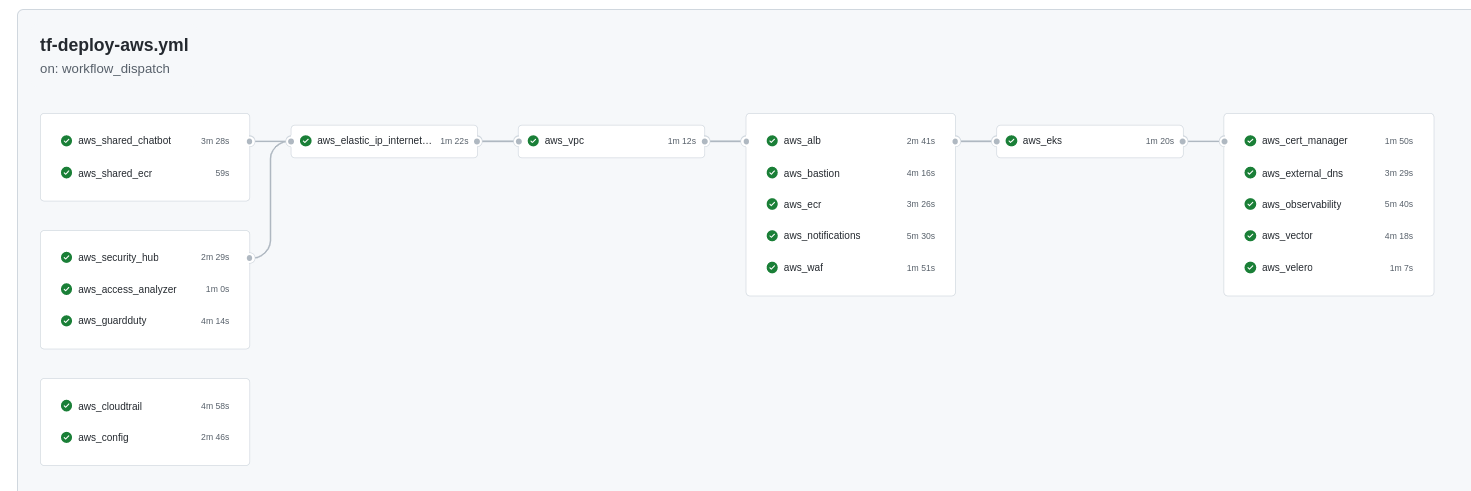
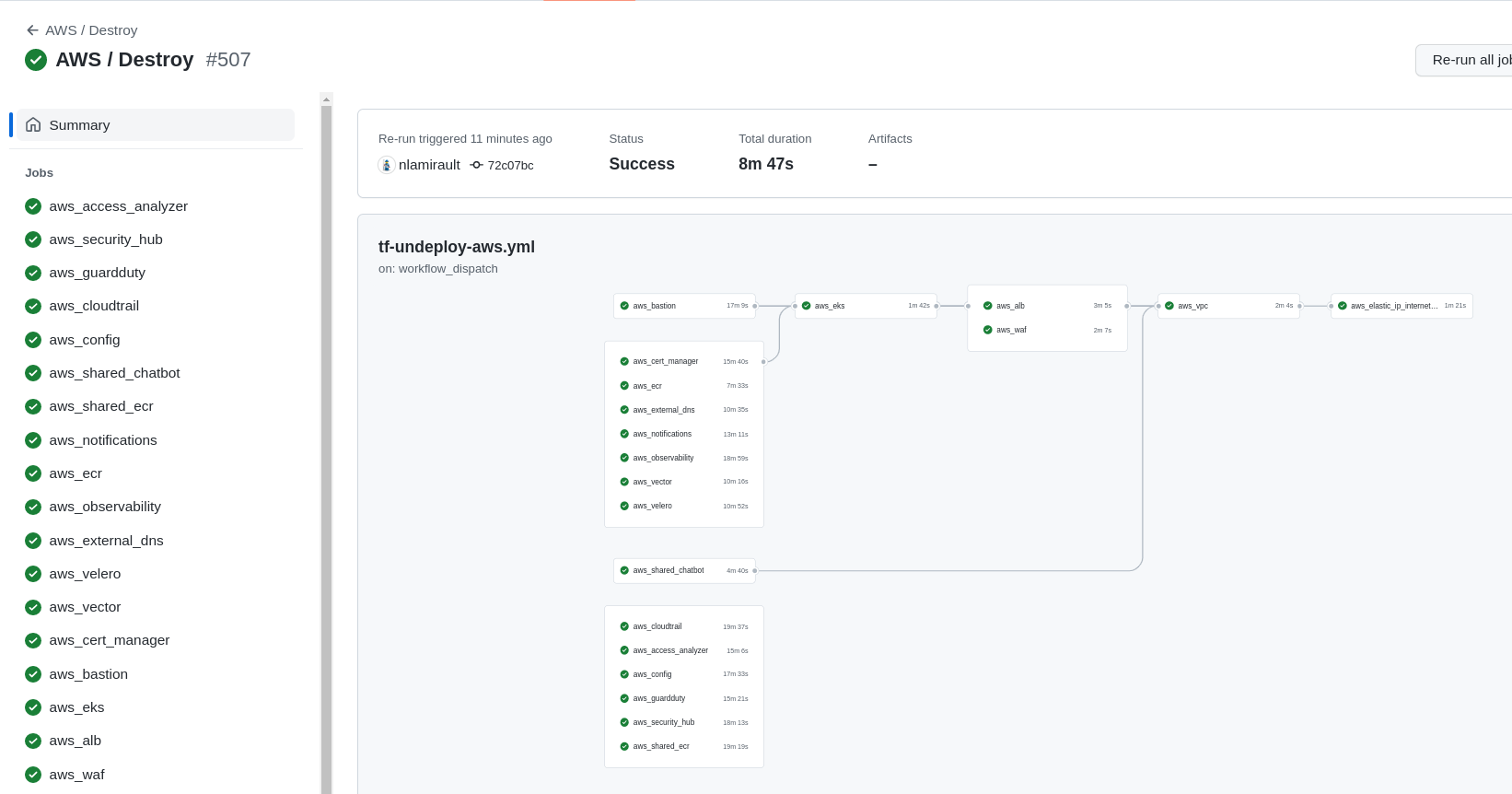
Github Actions with Terraform Cloud
could used to deploy and undeploy the infrastructure:
Authentication and authorization This section shows the how to setup Portefaix with authentication and authorization support in Microsoft Azure (AZURE)
❯ . ./portefaix.sh azure
[ Portefaix ]
Setup credentials
Done
Configure kubectl
❯ make -f hack/build/azure.mk azure-kube-credentials ENV = dev
❯ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
aks-core-19506595-vmss000000 Ready agent 8h v1.18.10
Gitops for Kubernetes Next: Gitops
Inspec Setup inspec is used to check infrastructure.
Check:
❯ make -f hack/build/azure.mk inspec-debug
Test infrastructure
────────────────────────────── Platform Details ──────────────────────────────
Name: azure
Families: cloud, api
Release: azure_mgmt_resources-v0.17.8
Execute tests:
❯ make -f hack/build/azure.mk inspec-test SERVICE = iac/azure/<SERVICE> ENV = dev
You could upload JSON results file to Heimdall Lite to display ressults
Microsoft Azure CIS Foundations You could perform tests accoring the CIS Microsoft Azure Foundations Security Benchmark :
❯ make -f hack/build/azure.mk inspec-cis ENV = dev
AKS
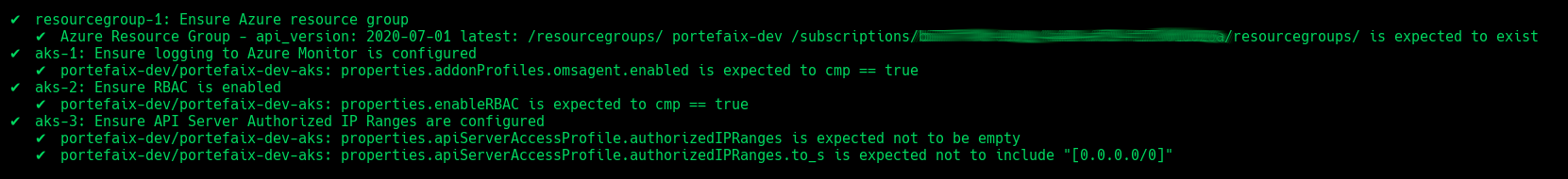
Code Description resourcegroup-1Check that resource group exists aks-1Ensure logging to Azure Monitor is configured aks-2Ensure RBAC is enabled aks-3Ensure API Server Authorized IP Ranges are configured
2.1.3 - Google Cloud Platform Running Portefaix on Google Cloud Platform
2.1.3.1 - Overview Portefaix architecture on Google Cloud Platform
2.1.3.2 - Install on Google Cloud Platform Running Portefaix on Google Cloud Platform
Organization Create a Google Cloud Organization using Google Workspace or Cloud Identity
See: https://cloud.google.com/resource-manager/docs/creating-managing-organization?hl=fr
Bootstrap Authenticate on the Google Cloud Platform:
❯ gcloud auth login
xxxxxxxxxx
❯ gcloud organizations list
DISPLAY_NAME ID DIRECTORY_CUSTOMER_ID
xxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxx
You could find the GCP_USER:
❯ gcloud auth list
Credentialed Accounts
ACTIVE ACCOUNT
* xxxxxxxxxxxx@portefaix.xyz
Create the Service Account on bootstrap project:
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-bootstrap-sa
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-bootstrap-credentials
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-bootstrap-iam GCP_ORG_ID = xxxx
Enable APIs on Bootstrap project:
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-bootstrap-apis
Bootstrap the organization:
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-organization-bootstrap GCP_ORG_ID = xxxxxxxxxxx GCP_USER = xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Then go to https://console.cloud.google.com/cloud-setup/organization to creates groups and create the billing account.
Then create the bootstrap project:
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-organization-project GCP_ORG_NAME = xxxx GCP_ORG_ID = xxxxxxxxxxx
Associate this project to the Billing Account (on GCP console or using gcloud):
gcloud alpha billing accounts projects link my-project --billing-account= xxxxxxx
Then create the bucket for boostraping the organization:
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-bucket GCP_ORG_NAME = xxxxxxx
Bootstrap:
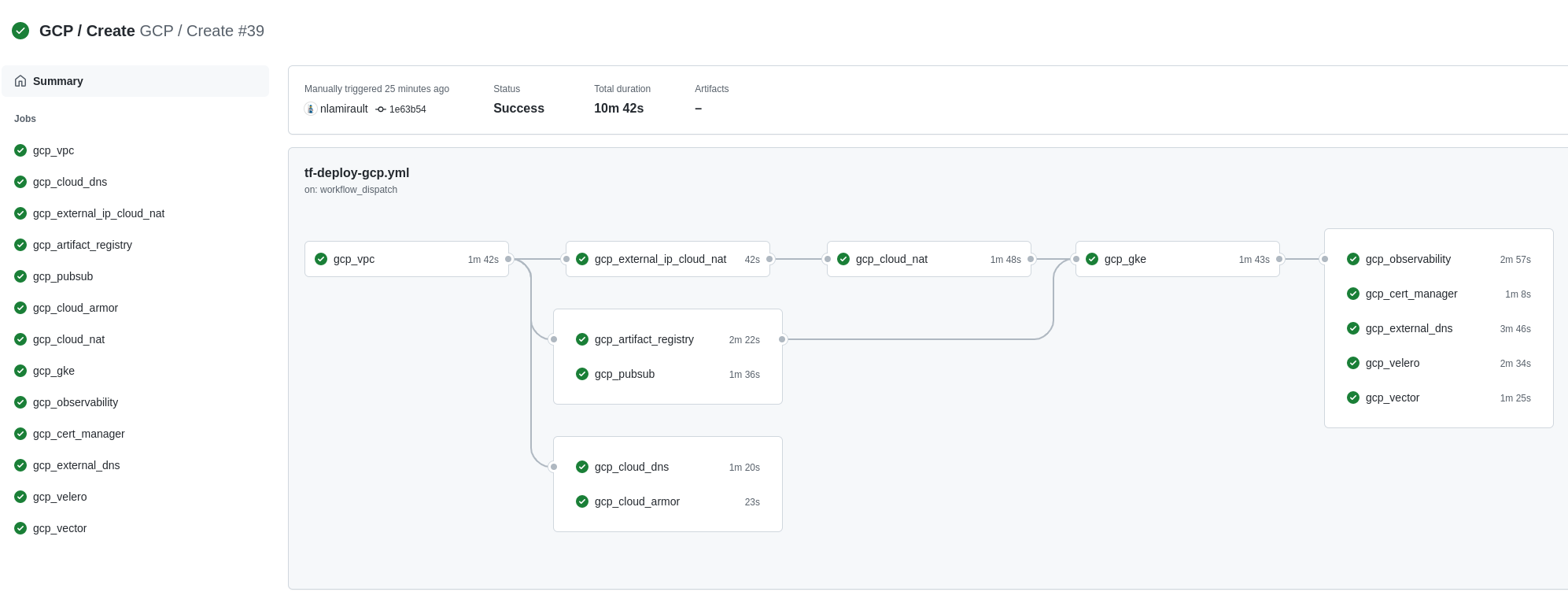
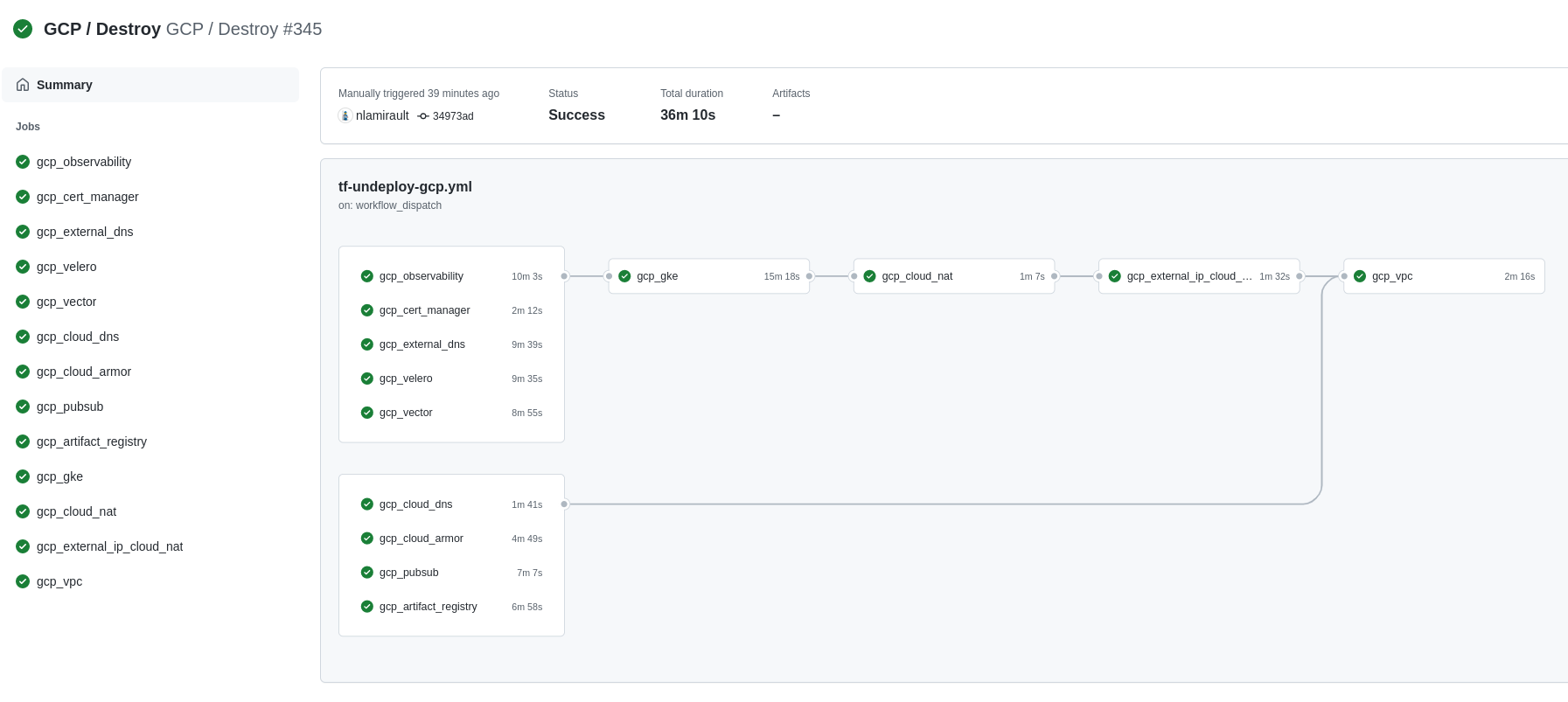
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/gcp/root ENV = main
Terraform Cloud is used as the remote backend. Github Actions perform tasks to deploy and undeploy the GCP infrastructure.
Configure Terraform Cloud workspaces:
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/gcp/terraform-cloud ENV = main
Authentication and authorization This section shows the how to setup Portefaix with authentication and authorization support in
Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Cloud IAP To enable Cloud IAP, you need first to configure the OAuth consent screen. If you still haven’t configured the OAuth
consent screen, you can do so with an email address and product name.
See https://support.google.com/cloud/answer/6158849?hl=en#zippy=%2Cuser-consent
Then creates the Oauth credentials .
Select the OAuth client ID from the Create credentials drop-down list and then select web application from the
application type. Next, add a name for your OAuth client ID and click create.
Gcloud
❯ . ./portefaix.sh gcp
[ Portefaix ]
Setup credentials
Done
Kubernetes
❯ make -f hack/build/azure.mk gck-kube-credentials CLOUD = gcp ENV = dev
❯ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
gke-xxxxxxxxxx-cluster-g-core-5d5d62be-tf15 Ready <none> 7h37m v1.18.10-gke.601
Gitops for Kubernetes Next: Gitops
Inspec inspec is used to check infrastructure:
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk inspec-debug
Test infrastructure
────────────────────────────── Platform Details ──────────────────────────────
Name: gcp
Families: cloud, api
Release: google-api-client-v0.34.1
Execute tests:
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk inspec-test SERVICE = iac/gcp/<SERVICE> ENV = dev
You could upload JSON results file to Heimdall Lite to display ressults
CIS Kubernetes Benchmark
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk inspec-gcp-kubernetes ENV = dev
GCP CIS You could perform tests accoring the GCP CIS :
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk inspec-cis ENV = dev
VPC
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk inspec-test SERVICE = iac/gcp/vpc ENV = dev
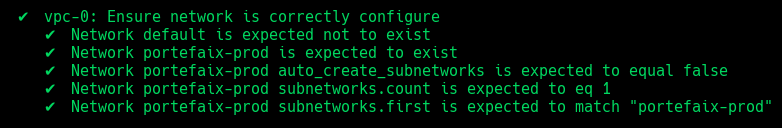
Code Description vpc-1Ensure default network is deleted vpc-2Ensure network is correctly configure
GKE
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-inspec-test SERVICE = iac/gcp/gke ENV = dev
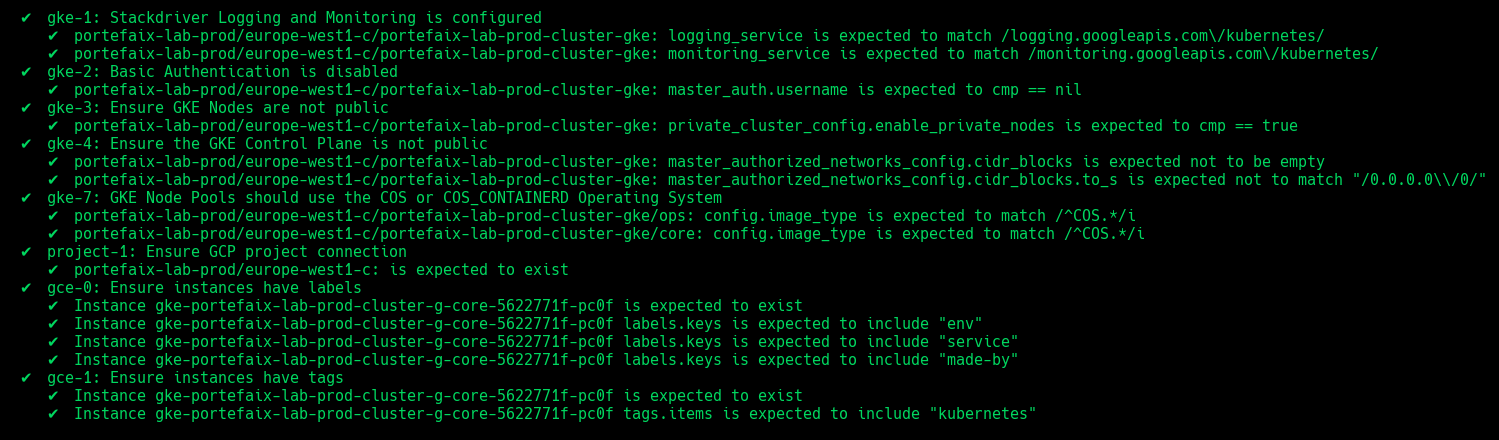
Code Description gke-1Stackdriver Logging and Monitoring is configured gke-2Basic Authentication is disabled gke-3Ensure GKE Nodes are not public gke-4Ensure the GKE Control Plane is not public gke-5Ensure the Network Policy managed addon is enabled gke-6Ensure OAuth Access Scopes and dedicated Service Accounts for node pools gke-7Ensure GKE Node Pools should use the COS or COS_CONTAINERD Operating System gke-8GKE Workload Identity should be enabled on all node pools gke-9GKE Shielded Nodes should be enabled on all NodePools gke-10Ensure instances have labels gke-11Ensure instances have tags
Sops
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-inspec-test SERVICE = iac/gcp/sops ENV = dev
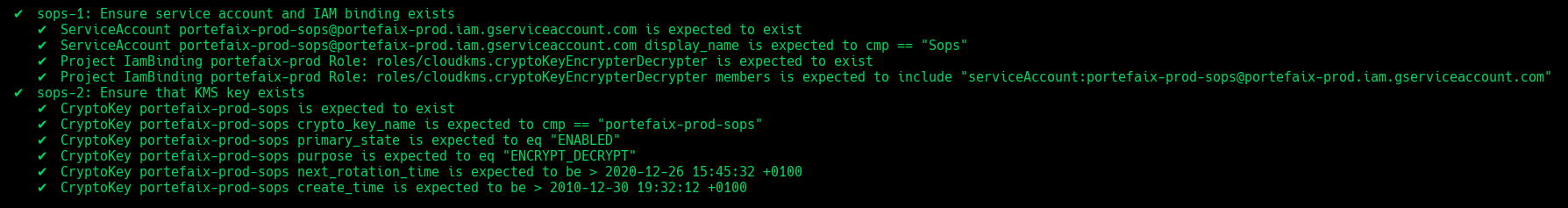
Code Description sops-1Ensure service account and IAM binding exists sops-2Ensure that Kms key exist
Observability
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-inspec-test SERVICE = iac/gcp/observability ENV = dev
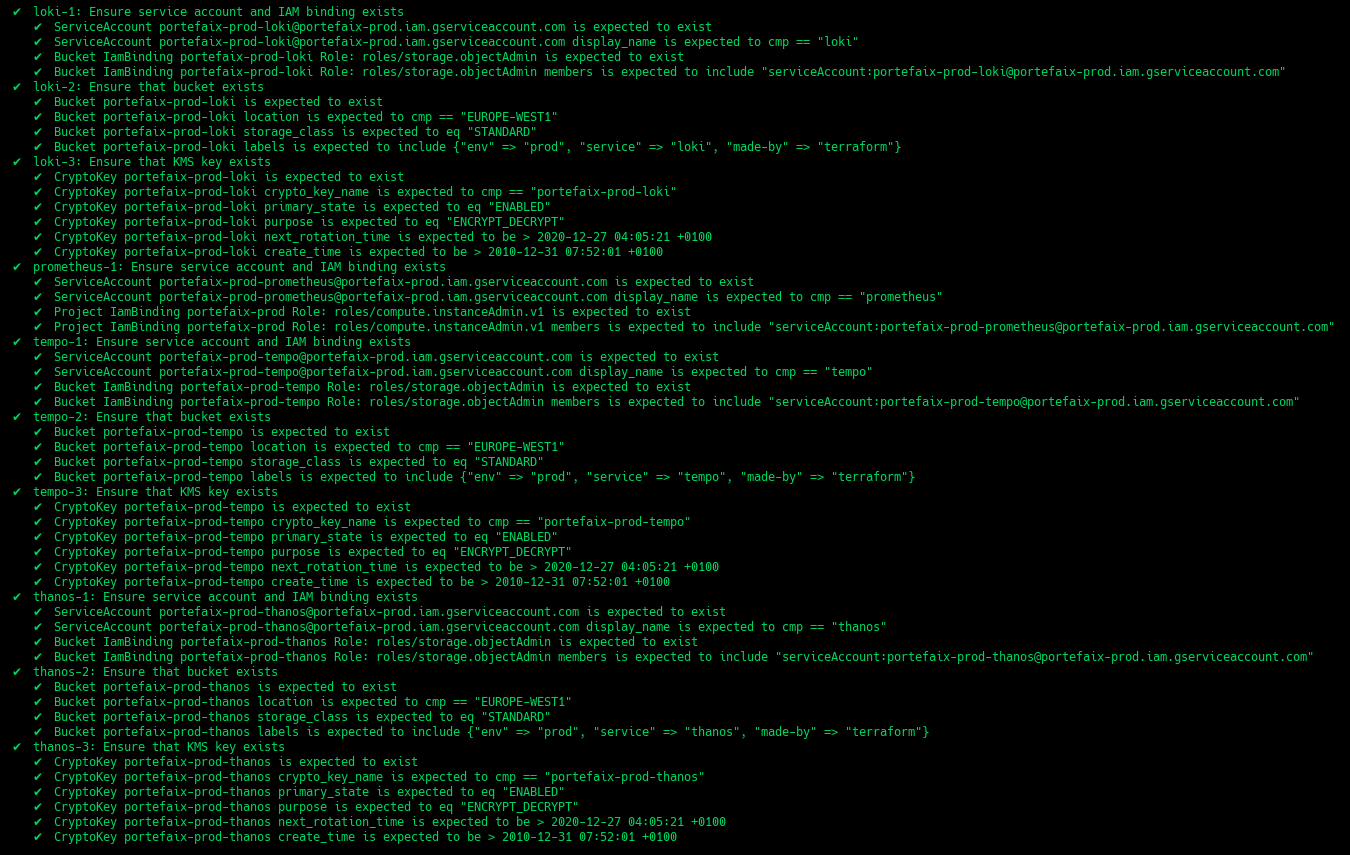
Code Description grafana-1Ensure service account and IAM binding exists prometheus-1Ensure service account and IAM binding exists thanos-1Ensure service account and IAM binding exists thanos-2Ensure that bucket exists and labels correcly set thanos-3Ensure that Kms key exist loki-1Ensure service account and IAM binding exists loki-2Ensure that bucket exists and labels correcly set loki-3Ensure that Kms key exist tempo-1Ensure service account and IAM binding exists tempo-2Ensure that bucket exists and labels correcly set tempo-3Ensure that Kms key exist
Velero
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-inspec-test SERVICE = iac/gcp/velero ENV = dev
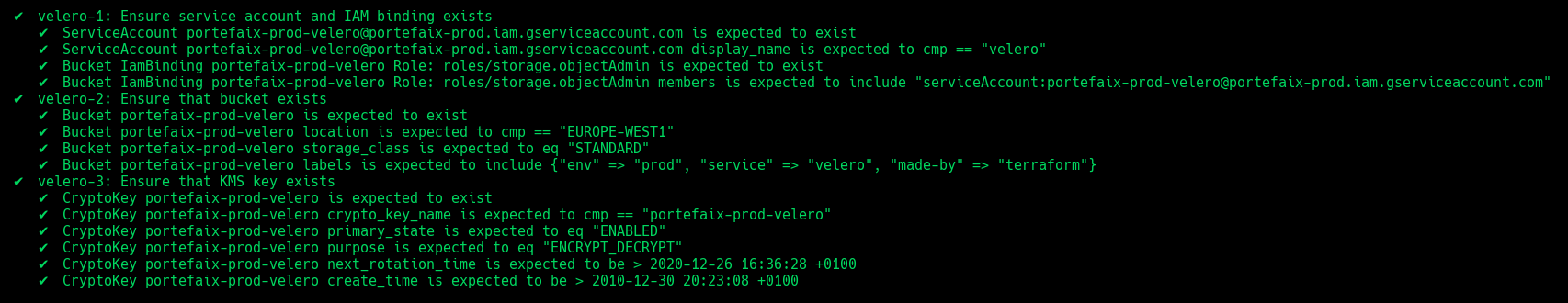
Code Description velero-1Ensure service account and IAM binding exists velero-2Ensure that bucket exists and labels correcly set velero-3Ensure that Kms key exist
Vector
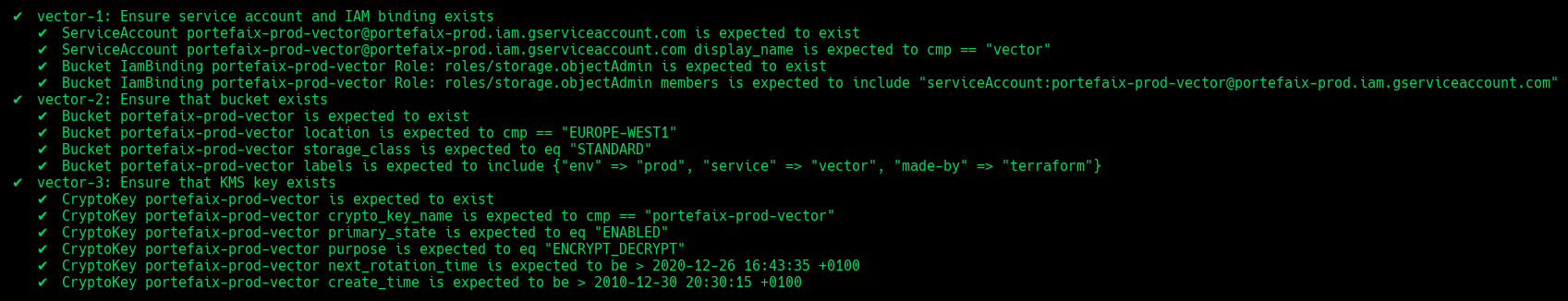
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-inspec-test SERVICE = iac/gcp/vector ENV = dev
Code Description vector-1Ensure service account and IAM binding exists vector-2Ensure that bucket exists and labels correcly set vector-3Ensure that Kms key exist
External-DNS
❯ make -f hack/build/gcp.mk gcp-inspec-test SERVICE = iac/gcp/external-dns ENV = dev
Code Description external_dns-1Ensure service account and IAM binding exists
2.1.4 - Alicloud Running Portefaix on Alicloud
2.1.4.1 - Overview Running Portefaix on Alibaba Cloud ACK
2.1.4.2 - Install on Alibaba Cloud Running Portefaix on Alibaba Cloud ACK
Setup Create an admin user, then API Keys.
And configure Portefaix environment file ${HOME}/.config/portefaix/portefaix.sh:
# Alicloud
function setup_alicloud() {
# Alicloud User: Portefaix Admin
export ALICLOUD_ACCESS_KEY = "xxxxxxxxxx"
export ALICLOUD_SECRET_KEY = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
export ALICLOUD_REGION = "eu-central-1"
# For Terraform Cloud
export TF_VAR_access_key = " ${ ALICLOUD_ACCESS_KEY } "
export TF_VAR_secret_key = " ${ ALICLOUD_SECRET_KEY } "
export TF_VAR_region = " ${ ALICLOUD_REGION } "
}
And load environment :
❯ . ./portefaix.sh alicloud
Create an OSS bucket for Terraform states:
❯ make -f hack/build/alicloud.mk aliyun-bucket-create ENV = staging
Create a TableStore instance:
❯ make -f hack/build/alicloud.mk aliyun-tablestore-create ENV = staging
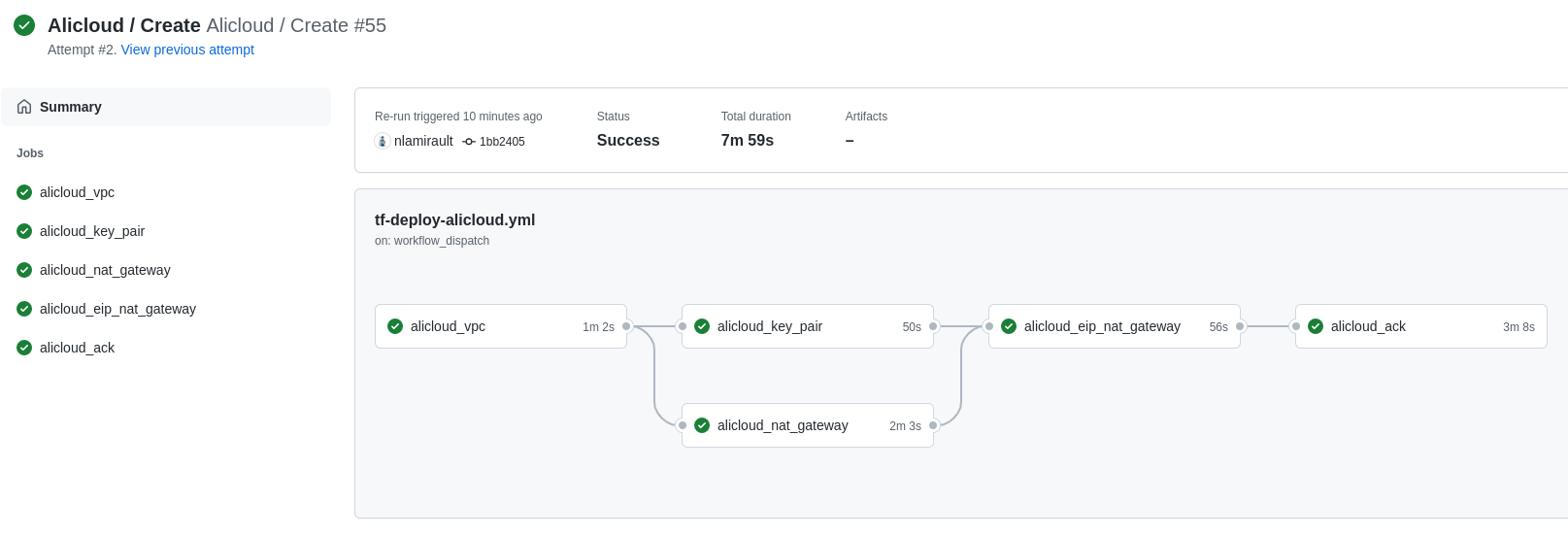
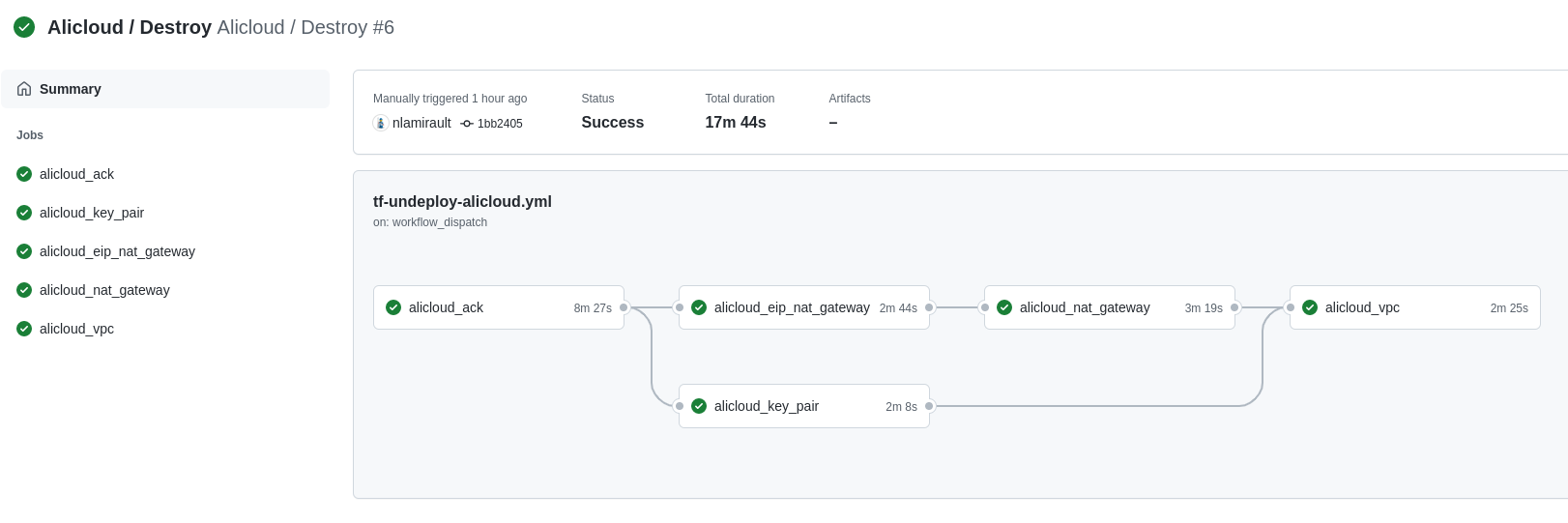
Terraform Cloud is used as the remote backend. Github Actions perform tasks to deploy the Alibaba Cloud infrastructure and undeploy:
Authentication and authorization This section shows the how to setup Portefaix with authentication and authorization support in Alibaba Cloud
❯ . ./portefaix.sh alicloud
[ Portefaix ]
Setup credentials
Done
Bastion
Work In Progress
Work In Progress
❯ make kubernetes-credentials CLOUD = alicloud ENV = staging
❯ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
Gitops for Kubernetes Next: Gitops
Inspec for Alicloud Setup Inspec is used to check infrastructure.
Check:
❯ make -f hack/build/alicloud.mk inspec-alicloud-debug
Execute tests:
Work In Progress CIS Kubernetes Benchmark
❯ make -f hack/build/alicloud.mk inspec-alicloud-kubernetes ENV = staging
2.1.5 - Scaleway Running Portefaix on Scaleway
2.1.5.1 - Overview Portefaix architecture on Scaleway
2.1.5.2 - Install on Scaleway Running Portefaix on Scaleway
Setup
# Scaleway
function setup_scaleway() {
export SCW_ACCESS_KEY = "xxxxx"
export SCW_SECRET_KEY = "xxxx"
export SCW_DEFAULT_PROJECT_ID = "xxxx"
export SCW_DEFAULT_ORGANIZATION_ID = " ${ SCW_DEFAULT_PROJECT_ID } "
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = " ${ SCW_ACCESS_KEY } "
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = " ${ SCW_SECRET_KEY } "
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION = "eu-west-3"
export AWS_REGION = "eu-west-3"
}
And load environment :
❯ . ./portefaix.sh scaleway
Create a S3 bucket for Terraform states:
❯ make -f hack/build/scw.mk scw-bucket ENV = sandbox
SKS
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = iac/scaleway/kapsule ENV = sandbox
Authentication and authorization This section shows the how to setup Portefaix with authentication and authorization support in Scaleway
❯ . ./portefaix.sh scaleway
[ Portefaix ]
Setup credentials
Done
❯ make kubernetes-credentials CLOUD = scaleway ENV = sandbox
Gitops for Kubernetes Next: Gitops
2.1.6 - Digital Ocean Running Portefaix on Digital Ocean
2.1.6.1 - Overview Portefaix architecture on Digital Ocean
2.1.6.2 - Install on Digital Ocean Running Portefaix on Digital Ocean
Setup
# Digital Ocean
function setup_digitalocean() {
export DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN = "xxxxxxxxxxxx"
export SPACES_ENDPOINT_URL = "fra1.digitaloceanspaces.com"
export SPACES_ACCESS_KEY_ID = "xxxxxxxxxx"
export SPACES_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = " ${ SPACES_ACCESS_KEY_ID } "
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = " ${ SPACES_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY } "
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION = "eu-west-3"
export AWS_REGION = "eu-west-3"
}
And load environment :
❯ . ./portefaix.sh digitalocean
Create a S3 bucket for Terraform states:
❯ make -f hack/build/digitalocean.mk exo-bucket ENV = dev
Authentication and Authorization This section shows the how to setup Portefaix with authentication and authorization support in Digital Ocean
❯ . ./portefaix.sh digitalocean
[ Portefaix ]
Setup credentials
Done
❯ make kubernetes-credentials CLOUD = digitalocean ENV = dev
Gitops for Kubernetes Next: Gitops
2.1.7 - Exoscale Running Portefaix on Exoscale
2.1.7.1 - Overview Portefaix architecture on Exoscale
2.1.7.2 - Install on Exoscale Running Portefaix on Exoscale
Setup
# AWS
export EXOSCALE_API_KEY = "xxxxx"
export EXOSCALE_API_SECRET = "xxxxxxxxxxx"
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = " ${ EXOSCALE_API_KEY } "
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = " ${ EXOSCALE_API_SECRET } "
And load environment :
❯ . ./portefaix.sh exoscale
Create a S3 bucket for Terraform states:
❯ make -f hack/build/exoscale.mk exo-bucket ENV = dev
SKS
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = iac/exoscale/sks ENV = dev
Authentication and authorization This section shows the how to setup Portefaix with authentication and authorization support in Exoscale
❯ . ./portefaix.sh exoscale
[ Portefaix ]
Setup credentials
Done
❯ make kubernetes-credentials CLOUD = exoscale ENV = dev
Gitops for Kubernetes Next: Gitops
2.1.8 - Civo Running Portefaix on Civo
2.1.8.1 - Overview Portefaix architecture on Civo
2.1.8.2 - Install on Civo Running Portefaix on Civo
Setup
# Civo
export CIVO_TOKEN = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
And load environment :
Work In Progress Network
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/civo/network ENV = dev
Kubernetes
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/civo/kubernetes ENV = dev
Authentication and authorization This section shows the how to setup Portefaix with authentication and authorization support in Civo
❯ . ./portefaix.sh civo
[ Portefaix ]
Flux
Pagerduty
TerraformCloud
Civo
✔ Done
❯ make -f hack/build/civo.mk civo-kube-credentials ENV = dev
❯ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k3s-portefaix-dev-civo-691a-de1391-node-pool-8c2e-859cq Ready <none> 6m29s v1.22.2+k3s1
Gitops for Kubernetes Next: Gitops
2.1.9 - IBM Cloud Running Portefaix on IBM Cloud
2.1.9.1 - Install on IBM Cloud Portefaix architecture on IBM Cloud
2.1.9.2 - Install on IBMCloud Running Portefaix on IBMCloud
Setup
# IBMCloud
export IAAS_CLASSIC_USERNAME = "xxxxxxxxxxxx"
export IC_API_KEY = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
export IAAS_CLASSIC_API_KEY = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
# For Terraform Backend S3
# See
And load environment :
❯ . ./portefaix.sh ibmcloud
Authentication:
❯ make -f hack/build/ibmcloud.mk ibmcloud-init ENV = staging
Then, generate the right set of HMAC credentials : documentation
❯ export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = "xxxxxxxxxx"
❯ export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
Create a S3 bucket for Terraform states:
❯ make -f hack/build/ibmcloud.mk ibmcloud-bucket-create ENV = staging
VPC
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/ibmcloud/vpc ENV = staging
IKS
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/ibmcloud/iks ENV = staging
Authentication and authorization This section shows the how to setup Portefaix with authentication and authorization support in IBMCloud
❯ . ./portefaix.sh ibmcloud
[ Portefaix ]
✔ Configuration file
✔ Flux
✔ PagerDuty
✔ Terraform Cloud
✔ IBMCloud
❯ make -f hack/build/ibmcloud.mk ibmcloud-kube-credentials CLOUD = ibmcloud ENV = staging
❯ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
10.242.0.10 Ready <none> 13m v1.22.7+IKS
10.242.0.7 Ready <none> 29m v1.22.7+IKS
10.242.128.10 Ready <none> 12m v1.22.7+IKS
10.242.128.7 Ready <none> 29m v1.22.7+IKS
10.242.64.6 Ready <none> 29m v1.22.7+IKS
10.242.64.8 Ready <none> 13m v1.22.7+IKS
Gitops for Kubernetes Next: Gitops
2.1.10 - Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Running Portefaix on OCI
2.1.10.1 - Install Portefaix Instructions for deploying Portefaix on Oracle Cloud
Setup Configure Oracle CLI. See https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/API/Concepts/apisigningkey.htm
Load environment :
Then authentication:
❯ make -f hack/build/oci.mk oci-authenticate ENV = staging
Create a new compartment
❯ make -f hack/build/oci.mk oci-compartment ENV = staging
Check compartement ID from output of the previous command and create a S3 bucket for Terraform states:
❯ make -f hack/build/oci.mk oci-bucket ENV = staging COMPARTMENT_ID = ocid1.compartment.oc1....
Bootstrap:
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/oci/root ENV = main
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/oci/terraform-cloud ENV = main
Terraform Cloud is used as the remote backend. Github Actions perform tasks to deploy the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Configure Terraform Cloud workspaces:
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/oci/terraform-cloud ENV = main
Authentication and authorization This section shows the how to setup Portefaix with authentication and authorization support in Exoscale
❯ . ./portefaix.sh exoscale
[ Portefaix ]
Setup credentials
Done
❯ make kubernetes-credentials CLOUD = exoscale ENV = dev
Gitops for Kubernetes Next: Gitops
2.1.10.2 - Overview Portefaix architecture on Orange Cloud Infrastructure
2.1.11.1 - Install Portefaix Instructions for deploying Portefaix infrastructure on Homelab
Operating System Setup operating system for Raspberry PI.
See: https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/
Or:
❯ sudo dd if = /dev/zero of = /dev/mmcblk0 conv = noerror status = progress
❯ sudo./hack/scripts/sdcard.sh <hostname> /dev/mmcblk0
Enable SSH :
❯ make -f hack/build/k3s.mk sdcard-mount ENV = homelab
❯ sudo touch /mnt/portefaix/boot/ssh
❯ echo portefaix-xxx | sudo tee /mnt/portefaix/root/etc/hostname
❯ make -f hack/build/k3s.mk sdcard-unmount ENV = homelab
Copy keys to each node:
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub pi@x.x.x.x
Ansible
❯ make ansible-deps SERVICE = ansible/k3s/machines CLOUD = k3s ENV = homelab
❯ make ansible-run SERVICE = ansible/k3s/machines CLOUD = k3s ENV = homelab
K3Sup Create the master :
❯ make -f hack/build/k3s.mk k3s-create ENV = homelab SERVER_IP = x.x.x.x EXTERNAL_IP = x.x.x.x
For each node, add it to the cluster, then add a label:
❯ make -f hack/build/k3s.mk k3s-join ENV = homelab SERVER_IP = x.x.x.x AGENT_IP = x.x.x.x EXTERNAL_IP = x.x.x.x
Authentication and authorization
❯ make kubernetes-credentials CLOUD = k3s ENV = homelab
Set labels:
❯ kubectl label node <NODE_NAME> node-role.kubernetes.io/worker= true
We add also these labels:
Label Description node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=true For core components node-role.kubernetes.io/lowcost=true For pocs, small applications, …
The nodes are in a NotReady state, due to the Pod Networking CNI plugin is not available.
Cilium must be installed:
❯ make bootstrap-crds ENV = homelab CLOUD = k3s
❯ make bootstrap-cilium ENV = homelab CLOUD = k3s
Then check nodes:
❯ kubectl get node -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
portefaix Ready control-plane,etcd,master 3h37m v1.30.2+k3s1 192.168.0.61 100.79.205.64 Ubuntu 24.04 LTS 6.8.0-36-generic containerd://1.7.17-k3s1
portefaix-1 NotReady lowcost,worker 155m v1.30.2+k3s1 192.168.0.208 100.115.34.57 Ubuntu 24.04 LTS 6.8.0-1005-raspi containerd://1.7.17-k3s1
portefaix-2 Ready lowcost,worker 154m v1.30.2+k3s1 192.168.0.116 100.126.100.42 Ubuntu 24.04 LTS 6.8.0-1005-raspi containerd://1.7.17-k3s1
portefaix-6 Ready infra,worker 3h21m v1.30.2+k3s1 192.168.0.233 100.111.218.32 Ubuntu 24.04 LTS 6.8.0-36-generic containerd://1.7.17-k3s1
portefaix-7 Ready infra,worker 3h18m v1.30.2+k3s1 192.168.0.250 100.86.220.99 Ubuntu 24.04 LTS 6.8.0-36-generic containerd://1.7.17-k3s1
and Cilium status:
❯ cilium status
/¯¯\
\_ _/¯¯\ Cilium: OK
\_ _/¯¯\_ _/ Operator: OK
/¯¯\_ _/¯¯\ Hubble: OK
\_ _/¯¯\_ _/ ClusterMesh: disabled
\_ _/
Deployment cilium-operator Desired: 1, Ready: 1/1, Available: 1/1
DaemonSet cilium Desired: 4, Ready: 4/4, Available: 4/4
Deployment hubble-relay Desired: 1, Ready: 1/1, Available: 1/1
Deployment hubble-ui Desired: 1, Ready: 1/1, Available: 1/1
Containers: cilium Running: 4
cilium-operator Running: 1
hubble-relay Running: 1
hubble-ui Running: 1
Cluster Pods: 4/4 managed by Cilium
Cloudflare R2 is used to store the Terraform states and for S3 buckets
Setup your Cloudflare Account ID, and your AWS credentials
function setup_cloudflare() {
echo_info "Cloudflare"
export CLOUDFLARE_ACCOUNT_ID = "xxxxxxxx"
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = "xxxxxxxxxxx"
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = "xxxxxxxxxxxx"
}
function setup_cloud_provider {
case $1 in
...
"k3s" )
setup_tailscale
setup_freebox
setup_cloudflare
;;
*)
echo -e " ${ KO_COLOR } Invalid cloud provider: $1 . ${ NO_COLOR } "
usage
;;
esac
}
The creates the bucket for Terraform:
❯ make -f hack/build/k3s.mk cloudflare-bucket-create ENV = homelab
[ portefaix] Create bucket for Terraform states
{
"Location" : "/portefaix-homelab-tfstates"
}
Configure DNS:
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/k3s/dns ENV = homelab
Creates the R2 buckets for Observability components:
❯ make terraform-apply SERVICE = terraform/k3s/observability ENV = homelab
Applications Next: Gitops
2.1.11.2 - Overview Portefaix architecture on Homelab
2.2 - Cloud Native Applications Learn about deploying applications into a Portefaix infrastructure
2.2.1 - GitOps Gitops managed applications
OpenGitops
2.2.2 - Argo-CD Gitops model for Kubernetes using ArgoCD
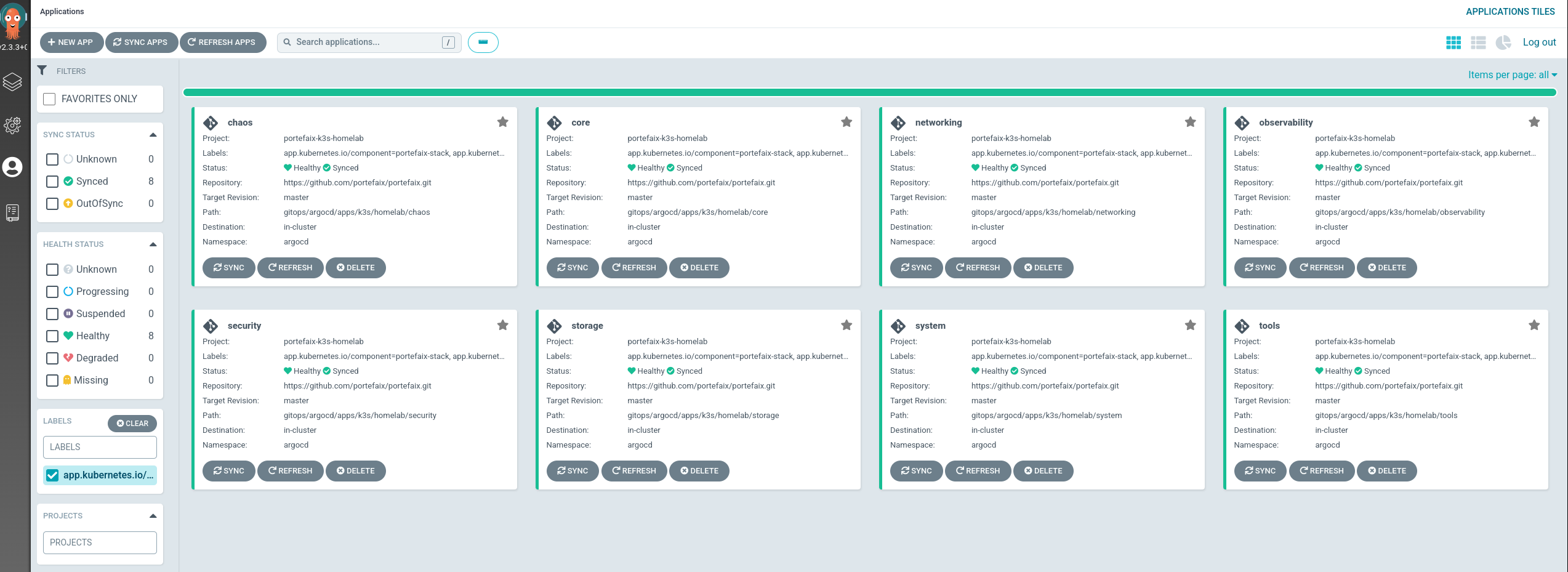
Organization gitops/argocd/bootstrap : Argo-CD deploymentgitops/argocd/stacks : Portefaix stacks : Argo-CD projects and applicationsgitops/argocd/apps/<CLOUD>/<ENVIRONMENT> : Argo-CD applications deployed into the Kubernetes clustergitops/argocd/charts : Helm charts configurationsTo configure the Helm charts, we use YAML files :
values.yaml: common configuration to all Kubernetes clustervalues-<CLOUD>-<ENVIRONMENT>.yaml : configuration of the Helm chart for a Kubernetes clusterBootstrap Argo-CD
❯ make bootstrap-argocd ENV = <environment> CLOUD = <cloud provider> CHOICE = helm
Stacks Install a stack into the cluster:
❯ make argocd-stack-install ENV = <environment> CLOUD = <cloud provider> STACK = <stack name>
Stacks:
Core System Networking Security Observability Chaos Tools You can list stack installed:
❯ helm list -A
NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
argo-cd argocd 1 2022-06-08 07:40:20.039787662 +0200 CEST deployed argo-cd-1.0.0 4.5.0
core argocd 1 2022-06-08 07:42:03.285558277 +0200 CEST deployed stack-0.1.0 0.1.0
system argocd 1 2022-06-08 07:41:21.749647011 +0200 CEST deployed stack-0.1.0 0.1.0
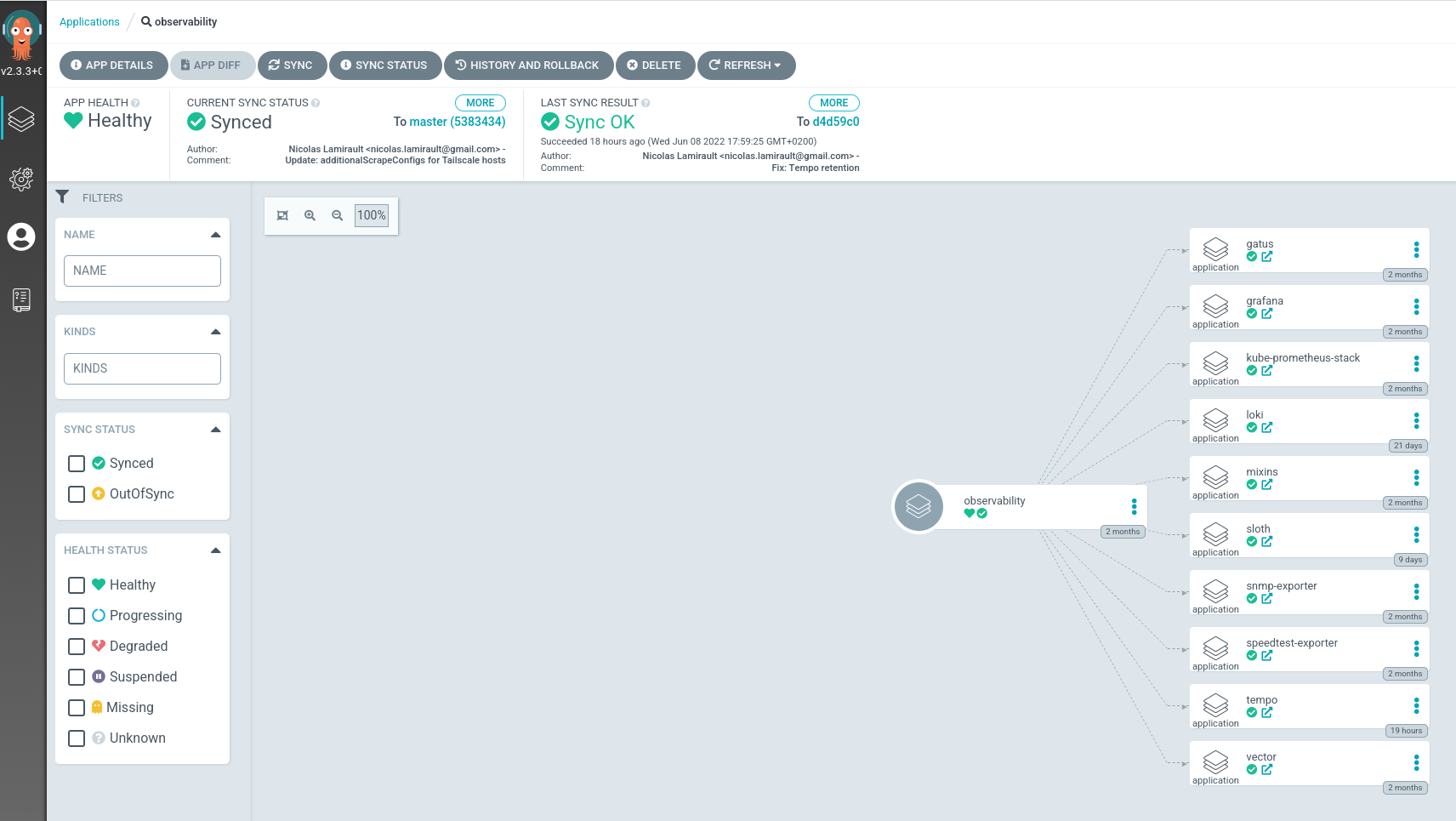
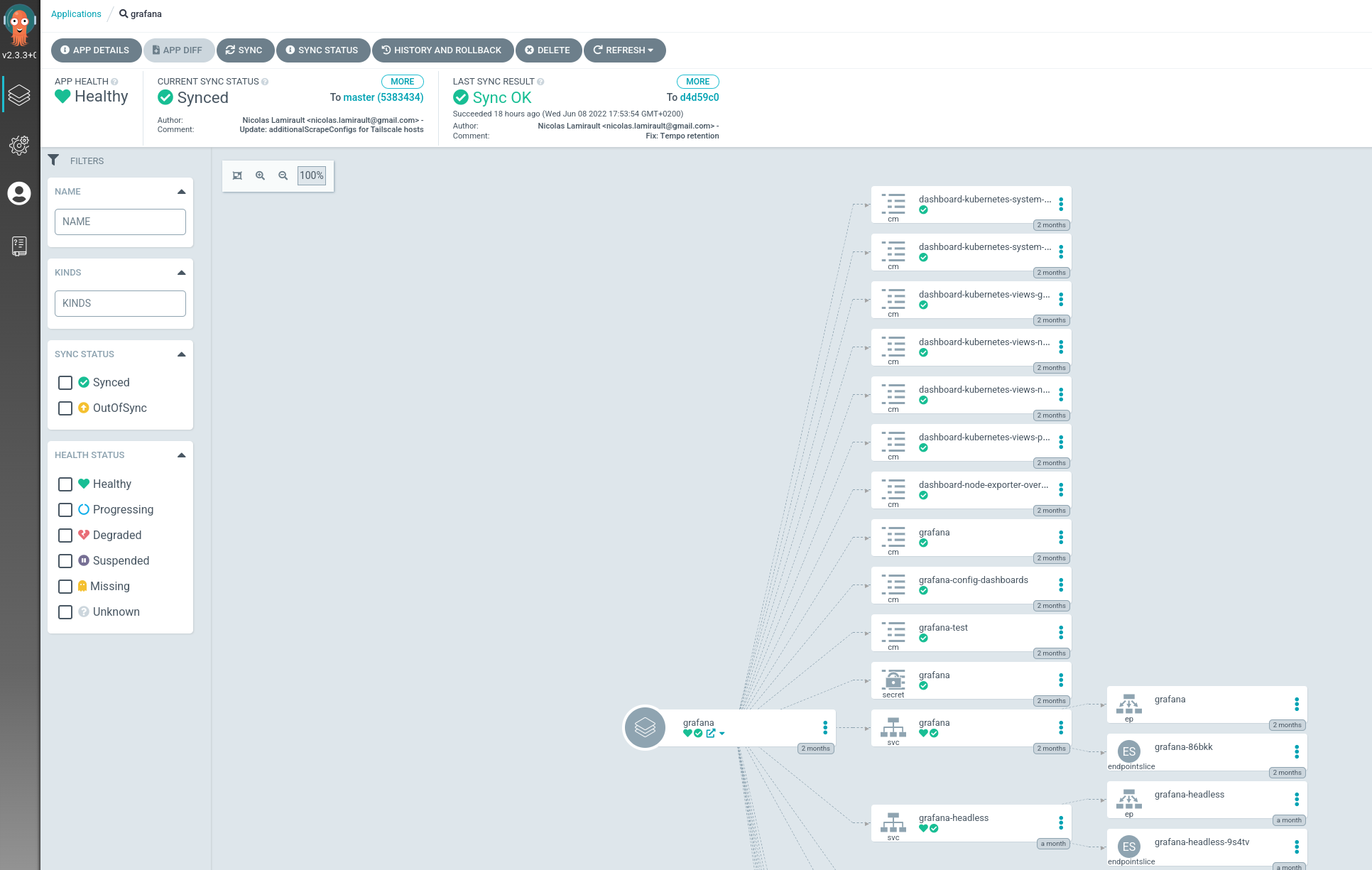
Argo-CD applications installs others Argo-CD applications:
Go to Argo-CD dashboard, you will see Argo-CD corresponding applications.
You can list Stack applications using the labels app.kubernetes.io/component: portefaix-stack
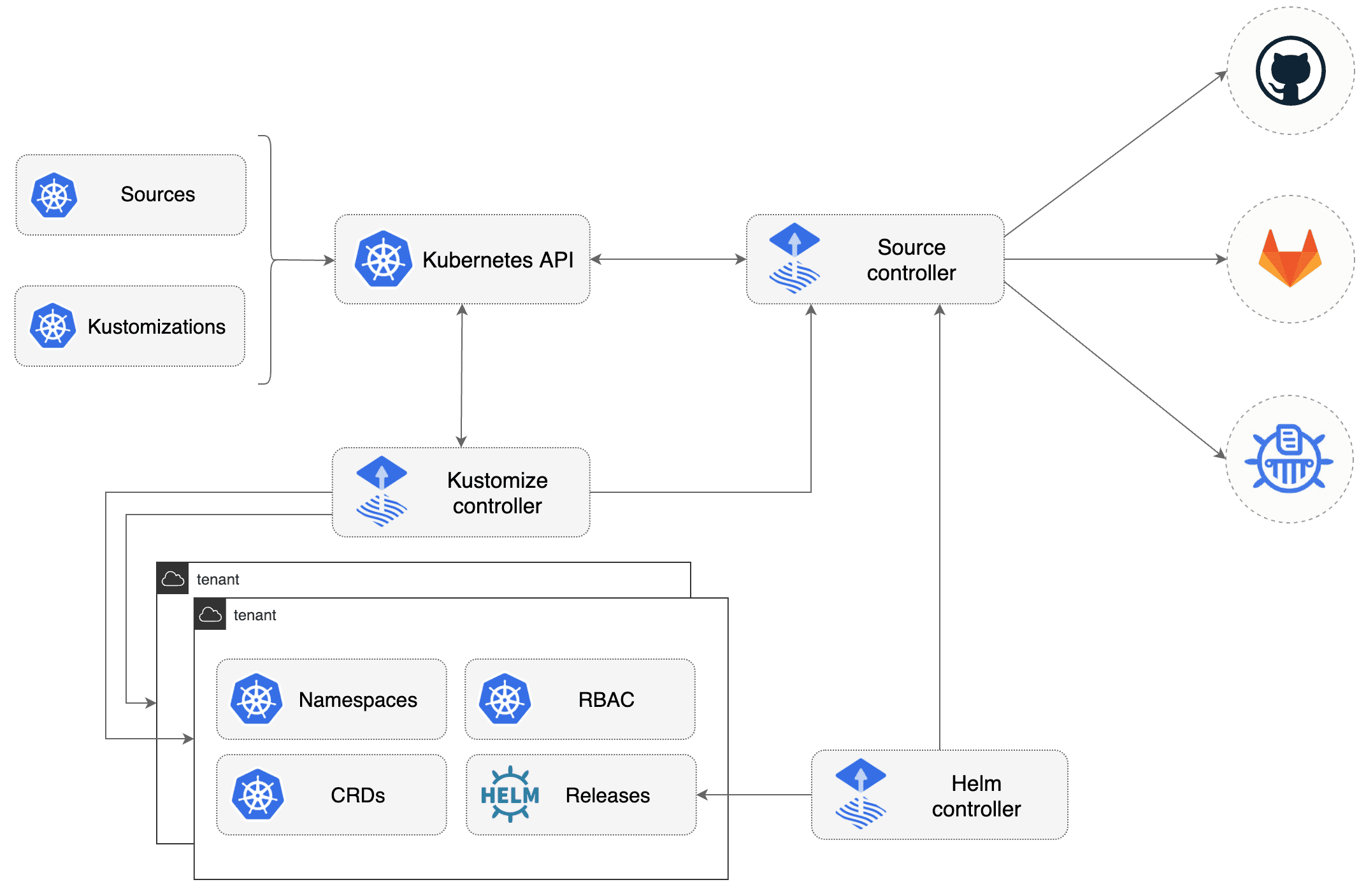
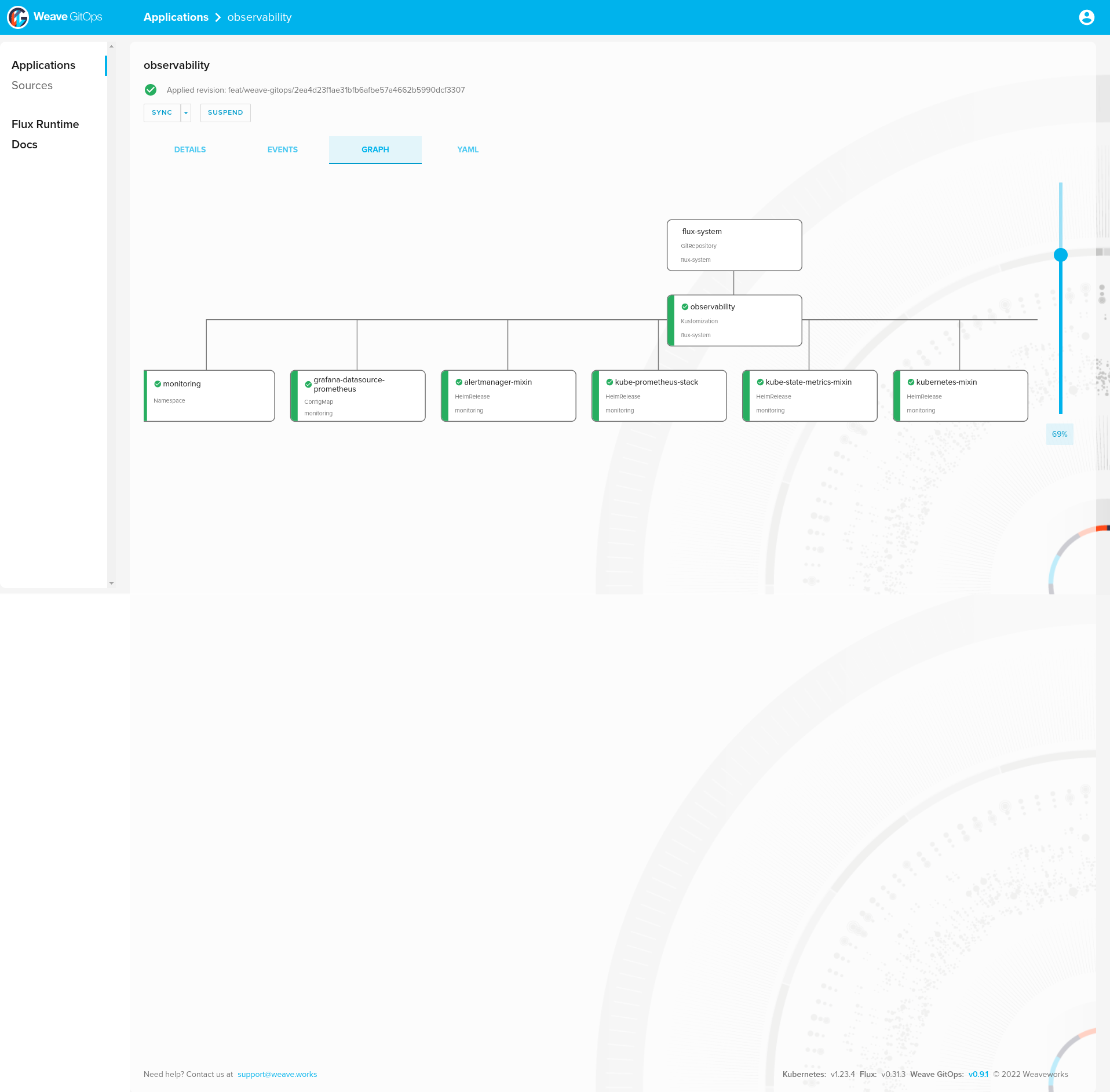
2.2.3 - FluxCD Gitops model for Kubernetes using Flux v2
Gitops model used is Flux v2
Organization Manifests files :
kubernetes/base directory contains manifests for all componentskubernetes/overlays/** directory contains Kustomize overlaysFlux components are deployed for each cluster on clusters/<CLOUD>/<ENV>/ :
clusters/<CLOUD>/<ENV>/flux-system : Flux core componentsclusters/<CLOUD>/<ENV>/*.yaml : Flux Kustomization files for componentsBootstrap FluxCD
❯ make bootstrap-fluxcd ENV = <environment> CLOUD = <cloud provider> BRANCH = <git branch to use>
Stacks You can list stack installed:
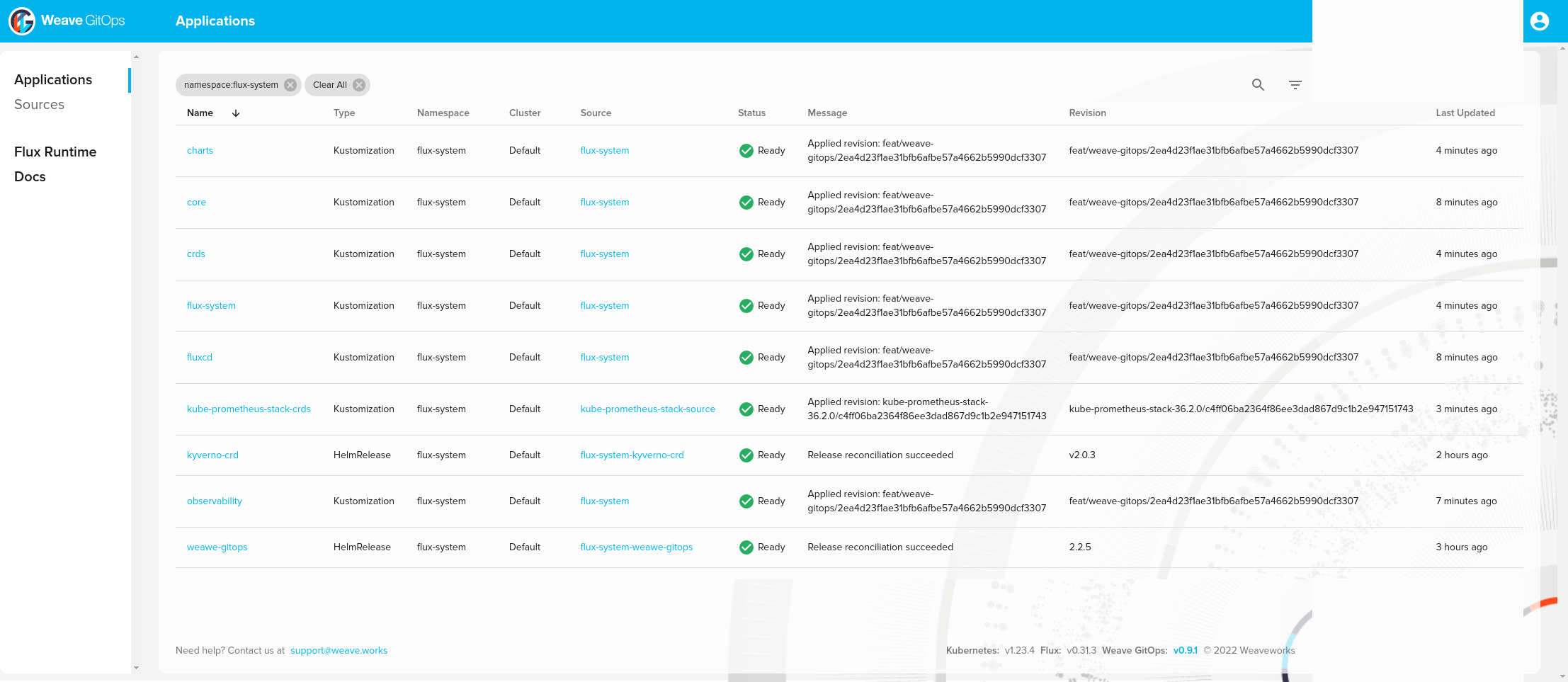
❯ kubectl -n flux-system get kustomization -l "app.kubernetes.io/component=portefaix-stack"
NAME AGE READY STATUS
core 107m True Applied revision: feat/weave-gitops/2ea4d23f1ae31bfb6afbe57a4662b5990dcf3307
observability 109m True Applied revision: feat/weave-gitops/2ea4d23f1ae31bfb6afbe57a4662b5990dcf3307
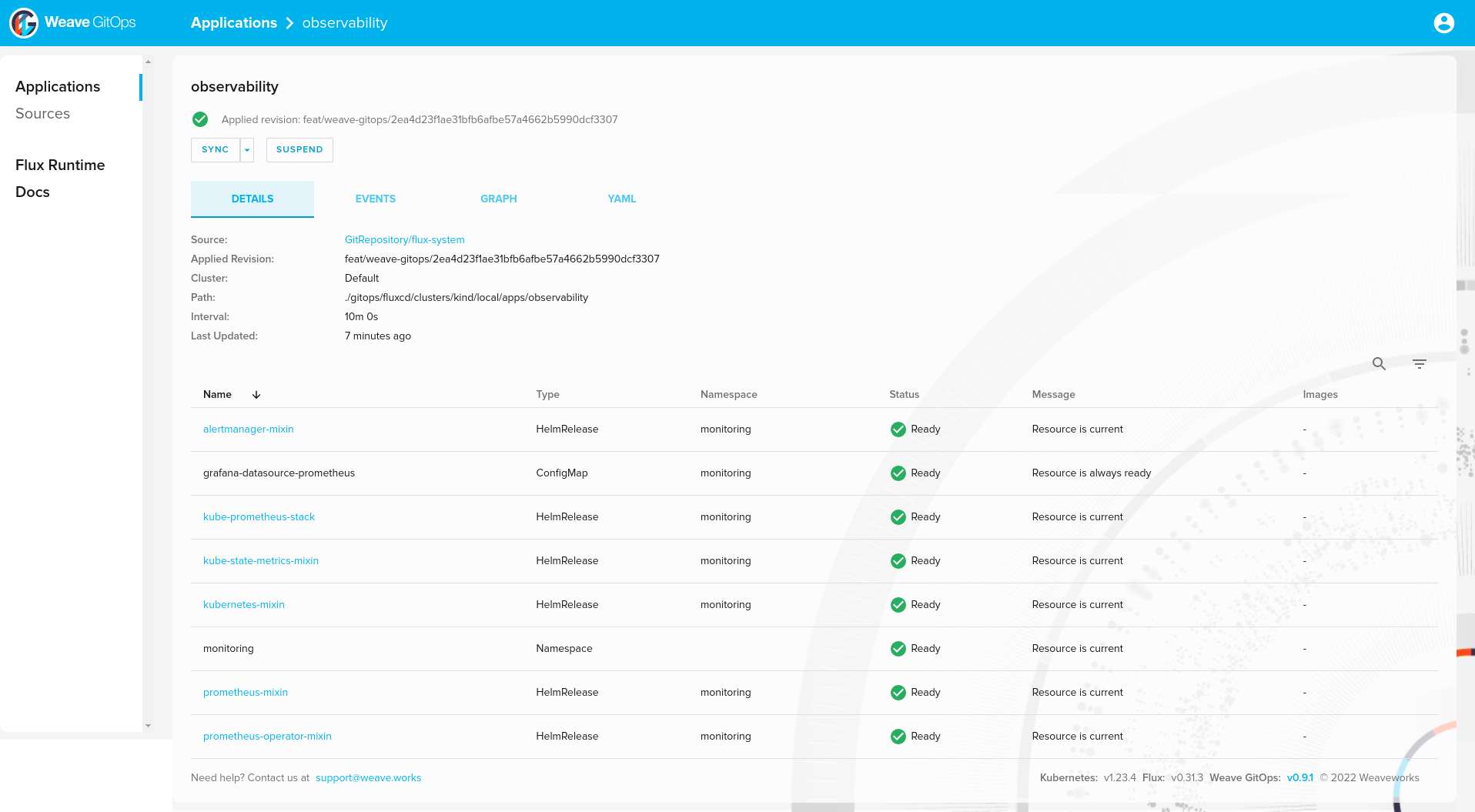
And Helm releases:
❯ helm list -A
NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
alertmanager-mixin monitoring 1 2022-08-08 10:57:51.540267795 +0000 UTC deployed alertmanager-mixin-0.6.0 0.23.0
kube-prometheus-stack monitoring 1 2022-08-08 10:57:52.701498295 +0000 UTC deployed kube-prometheus-stack-35.0.3 0.56.0
kube-state-metrics-mixin monitoring 1 2022-08-08 10:57:52.285323133 +0000 UTC deployed kube-state-metrics-mixin-0.10.0 2.2.4
kubernetes-mixin monitoring 1 2022-08-08 10:57:52.528376605 +0000 UTC deployed kubernetes-mixin-0.8.0 0.8.0
kyverno flux-system 1 2022-08-08 09:00:31.649605165 +0000 UTC deployed kyverno-crds-v2.0.3 v1.4.3
metrics-server kube-system 1 2022-08-08 10:57:41.851963826 +0000 UTC failed metrics-server-3.8.2 0.6.1
prometheus-mixin monitoring 1 2022-08-08 10:57:53.019370201 +0000 UTC deployed prometheus-mixin-0.10.0 2.31.1
prometheus-operator-mixin monitoring 1 2022-08-08 10:57:53.815678548 +0000 UTC deployed prometheus-operator-mixin-0.8.0 0.52.1
weawe-gitops flux-system 1 2022-08-08 07:49:32.97390968 +0000 UTC deployed weave-gitops-2.2.5 v0.9.1
Secrets File Create a Kubernetes secret file from sensitive file.
Ex: for Thanos configuration :
❯ cat .secrets/aws/object-store.yaml
type : S3
config :
bucket : xxxxxxxxxxx
endpoint : s3.eu-west-3.amazonaws.com
region : eu-west-3
❯ make kubernetes-secret NAME = thanos-object-storage NAMESPACE = monitoring FILE = .secrets/aws/object-store.yaml > thanos-object-storage.yaml
Encrypt Encrypt the file using Sops:
❯ make sops-encrypt ENV = staging CLOUD = aws FILE = thanos-object-storage.yaml
You can now safely store this file into Git.
❯ mv thanos-object-storage.yaml kubernetes/overlays/staging/monitoring/thanos/
Decrypt Check you can decrypt the file:
❯ make sops-decrypt FILE = kubernetes/overlays/staging/monitoring/thanos/thanos-object-storage.yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
object-store.yaml: xxxxxxxxxxx
kind: Secret
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: thanos-object-storage
namespace: monitoring
CI/CD AGE
Work In Progress PGP Generate a GPG key with OpenPGP without specifying a passphrase:
❯ gpg --full-generate-key
Real name: nlamirault
Email address: nlamirault@users.noreply.github.com
Comment:
You selected this USER-ID:
"nlamirault <nlamirault@users.noreply.github.com>"
Change ( N) ame, ( C) omment, ( E) mail or ( O) kay/( Q) uit? O
Retrieve the GPG key ID:
❯ gpg --export-secret-keys \
Add this output into a Github Secret SOPS_GPG_KEY.
On the e2e Github Action workflow, we create a Kubernetes secret sops-gpg
which will be used by Flux.
3 - Contributing to Portefaix Guides and requirements for contributing to Portefaix
3.1 - Overview: Contributing to Portefaix Guides and requirements for contributing to Portefaix
We welcome contributions to Portefaix! Contributions can come in different ways such as contributing code or improving the documentation. This page provides an overview of the different ways you can contribute to Portefaix.
Check out the Portefaix Community page to learn about the different ways you can engage with the Portefaix community.
GitHub If you would like to file Issues, access the source code, or use Codespaces please visit the Portefaix GitHub organization .
Contributing to Portefaix Check out the following table to learn where and how you can contribute:
3.2 - How-To: Contribute to the Portefaix documentation How to contribute to the Portefaix documentation
The Portefaix docs are built on Hugo with the Docsy theme. GitHub Actions are used to build and deploy the docs upon each PR.
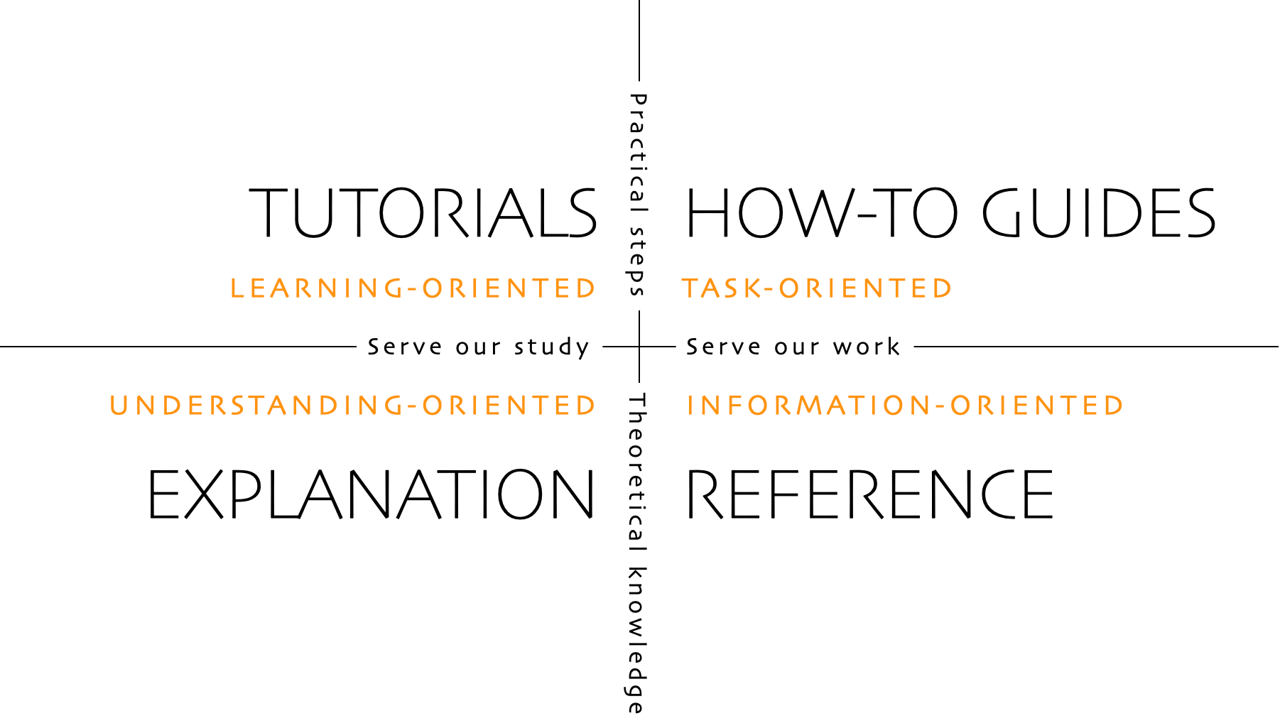
Portefaix uses the Diátaxis framework for its documentation:
Follow the guidance on this page to learn how to get started, how to contribute, and how to use the Diátaxis framework to create new docs.
Types of docs There are 4 types of docs in Portefaix:
Tutorial - Tutorials are lessons that take the reader by the hand through a series of steps to complete a project or understand specific processes. The primary purpose is to educate users through a step-by-step approach, ensuring they can successfully complete a task or acquire a new skill. See Diátaxis .How-To - How-To Guide gives a concise set of instructions as it is geared towards people who have some experience. It assumes the user already has the experience and they just want to get a particular task done. See Diátaxis .Explanation - Explanation widens the understanding of a reader about a subject. It provides users with a deeper understanding of concepts, principles, or features. See Diátaxis .Reference - A reference doc is a detailed description of a specific feature or capability of the project. It assumes the reader has a basic understanding of the project and its concepts. For more information on reference docs, see Diátaxis .Overall:
Tips and tricks Any contribution must ensure not to break the website build. The way Hugo builds the website requires following the below guidance.
Front-matter Front-matter is what takes regular markdown files and upgrades them into Hugo-compatible docs for rendering into the nav bars and ToCs.
Every page needs a section at the top of the document like this:
---
type : docs
title : "TITLE FOR THE PAGE"
linkTitle : "SHORT TITLE FOR THE NAV BAR"
weight : (number)
description : "1+ SENTENCES DESCRIBING THE ARTICLE"
categories : "TYPE OF THE DOCUMENT"
tags : "METADATA ON THE DOCUMENT"
---
Referencing other pages Hugo ref and relref shortcodes are used to reference other pages and sections. It also allows the build to break if a page is incorrectly renamed or removed.
This shortcode, written inline with the rest of the markdown page, will link to the _index.md of the section/folder name:
This shortcode will link to a specific page:
Note that all pages and folders need to have globally unique names in order for the ref shortcode to work properly. If there are duplicate names the build will break and an error will be thrown.
Referencing sections in other pages To reference a specific section on another page, add #section-short-name to the end of your reference.
As a general rule, the section’s short name is the text of the section title, all lowercase, with spaces changed to “-”. You can check the section’s short name by visiting the website page, clicking the link icon (🔗) next to the section, and see how the URL renders in the nav bar. The content after the “#” is your section shortname.
As an example, for this specific section, the complete reference to the page and section would be:
{{< ref " contributing-docs . md # referencing-sections-in-other-pages " > }}
References 4 - Portefaix reference documentation Detailed reference documentation on various Portefaix components
4.1 - Components The components used by Portefaix
Infrastructure management Terraform : Bootstraps and manages the cloud provider infrastructure.Crossplane : Kubernetes-native infrastructure management.Cluster management Argo CD : Reconciles kubernetes clusters with this repository.Kyverno : Policy engine supporting validate, mutate, generate, and cleanup rules.Renovate : Automatic updates for applications via pull requests.Secrets Networking Security Falco : The Cloud Native Runtime SecurityAuthentik : Identity Provider.Trivy : Kubernetes and container vulnerability scanner.Tetragon : eBPF-based security observability and runtime enforcement.Observability Grafana : Visualization platform.Prometheus : Monitoring system.Loki : Log aggregation system.Tempo : High-scale distributed tracing backendMimir : Horizontally scalable TSDB for long-term storage for PrometheusAlloy : The OpenTelemetry Distribution from GrafanaStorage 4.2 - Hub The Portefaix Hub for Helm charts
Portefaix Hub Portefaix Hub is the Helm charts repository of the Portefaix project.
All charts could be find on Artifact Hub
4.3 - Policies The Portefaix policies
Portefaix Policies contains Kubernetes policies for Kyverno or Open Policy Agent .
Kyverno PORTEFAIX-C0001 - Container must not use latest image tagPORTEFAIX-C0002 - Container must set liveness probePORTEFAIX-C0003 - Container must set readiness probePORTEFAIX-C0004 - Container must mount secrets as volumes, not enviroment variablesPORTEFAIX-C0005 - Container must drop all capabilitiesPORTEFAIX-C0006 - Container must not allow for privilege escalationPORTEFAIX-C0008 - Container resource constraints must be specifiedPORTEFAIX-M0001 - Metadata must set recommanded Kubernetes labelsPORTEFAIX-M0002 - Metadata should have a8r.io annotationsPORTEFAIX-M0003 - Metadata should have portefaix.xyz annotationsPORTEFAIX-P0002 - Pod must run without access to the host IPCPORTEFAIX-P0003 - Pod must run without access to the host networkingPORTEFAIX-P0004 - Pod must run as non-rootPORTEFAIX-P0005 - Pod must run without access to the host PIDOpen Policy Agent PORTEFAIX-C0001: Container must not use latest image tagPORTEFAIX-C0002: Container must set liveness probePORTEFAIX-C0003: Container must set readiness probePORTEFAIX-C0004: Container must mount secrets as volumes, not enviroment variablesPORTEFAIX-C0006: Container must not allow for privilege escalationPORTEFAIX-C0008: Container must define resource contraintesPORTEFAIX-M0001: Metadata should contain all recommanded Kubernetes labelsPORTEFAIX-M0002: Metadata should have a8r.io annotationsPORTEFAIX-M0003: Metadata should have portefaix.xyz annotationsPORTEFAIX-N0001: Disallow Default Namespace4.4 - KRM The Kubernetes Resources Model deployed into Portefaix
Kubernetes Resources Model KRM could be use to deploy infrastructure on cloud providers.
GCP
Work In Progress Config Connector
AWS
Work In Progress AWS Controller for Kubernetes
Azure
Work In Progress Azure Service Operator
4.5 - Inspec The Inspec profiles for Portefaix
GCP
Work In Progress AWS
Work In Progress Azure
Work In Progress 5 - Portefaix Community Information about the Portefaix community
5.1 - Portefaix Community Information about the Portefaix community
Welcome to the Portefaix community!
How can I get involved? If you are interested in contributing to the Portefaix project, please visit the Contributing to Portefaix page for more information.